Imagine a world where inventory counts itself, shipments are tracked in real-time, and payments are made with just a wave of your hand. This is the power of RFID, a technology revolutionizing industries worldwide.
What is RFID full form?
Some people may want to know what is RFID? or what is the full form of RFID card?
RFID stands for Radio-Frequency Identification and RFID cards are cards that use radio waves to identify people or objects. if you’ve ever used a contactless payment card or skipped the line at a toll booth with an E-ZPass, you’ve experienced its magic firsthand! It’s like a supercharged barcode, but instead of needing a line of sight and a scanner, an RFID tag uses radio waves to identify and track items from a distance – even through walls!
In this guide, we’ll explore how RFID works and why it’s becoming indispensable for businesses.
RFID Tags vs. Smart Labels: Two Peas in a Pod, or Apples and Oranges?
RFID tags are the heart of the system, tiny microchips with antennas that store and transmit information. Think of them like little digital passports carrying details about the object they’re attached to.
- Example: In 2023, Zara implemented the RFID tag in over 2,000 stores, resulting in a 15% increase in inventory accuracy and a 50% reduction in out-of-stock items. That’s like always having your favorite shirt in your size, no matter how popular it is!
Smart labels, on the other hand, are a hybrid of RFID and barcodes. They offer the best of both worlds: the speed and convenience of RFID for quick scanning, plus the visual information of a barcode for easy human readability.
- Did You Know? The global smart label market is projected to reach a staggering $55.55 billion by 2030, driven by the increasing demand for efficient inventory management and supply chain visibility. Talk about a smart investment!
The RFID Family Tree: Meet the Different Types
Like any good family, RFID systems come in different shapes and sizes, each with its own unique personality and talents:
1. Passive RFID:
These tags are like wallflowers at a party, quiet and unassuming until someone strikes up a conversation. They have no internal power source and rely on the reader’s signal to wake up and respond. They’re small, inexpensive, and perfect for applications like inventory management and access control.
Real-World Application: The average cost of a passive RFID tag is around $0.10, making it a cost-effective solution for tracking high-volume, low-value items. It’s like having a personal assistant for your sock drawer, ensuring you never lose another pair!
2. Active RFID:
These tags are the life of the party, constantly broadcasting their presence with their own built-in battery. They have a longer read range and can transmit data more frequently, making them ideal for tracking high-value assets and vehicles in real-time.
Industry Impact: Active RFID tags have revolutionized the logistics industry, with DHL reporting a 95% reduction in search time for misplaced shipments. It’s like having a GPS tracker for every package, ensuring your deliveries arrive on time, every time.
3. Semi-Passive RFID:
These tags are a bit of a hybrid, combining the best of both worlds. They have a battery to power their internal circuitry but still rely on the reader’s signal for communication. They offer a longer read range than passive tags and a longer lifespan than active tags, making them suitable for applications like industrial monitoring and environmental sensing.
Fun Fact: Semi-passive RFID tag is commonly used to monitor the temperature and humidity of perishable goods during transportation, ensuring they arrive fresh and safe to consume. It’s like having a personal chef for your groceries, keeping everything at the perfect temperature!
How does it work? It’s like a high-tech game of Marco Polo.
Imagine a playful game of Marco Polo but with radio waves instead of voices. The RFID reader shouts out “Marco!” by sending out a radio signal. Any RFID tags within range respond with a cheerful “Polo!” sending back their unique identification information. This data then zips over to a computer for further processing. It’s like a silent conversation between objects happening all around us!
How Does RFID Work?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) systems operate using a combination of three key components: tags, readers, and antennas. Together, they enable seamless data collection and communication. Here’s how the process works:
- RFID Tags: These are small devices embedded with a microchip and antenna. The microchip stores data about an object, such as its product details, serial number, or location. Tags can be classified as passive (powered by the reader’s signal), active (battery-powered), or semi-passive (a mix of both).
- RFID Readers: Readers emit radio waves to detect and activate nearby RFID tags. Once activated, the tags transmit their stored data back to the reader for processing.
- Antennas: Antennas facilitate communication between tags and readers by transmitting radio signals. They play a crucial role in ensuring accurate and efficient data exchange across varying distances.
After the data is collected by the reader, it is sent to a connected database or software system for analysis. This enables real-time tracking, automation, and actionable insights for businesses across industries.
Fun Fact:
Most RFID tags can read from 10 to 20 feet away, but some special tags can read from up to several hundred feet away! That’s like being able to find your lost keys from across a football field.
Now that we understand how RFID works, let’s explore its transformative impact on various industries through real-world applications.
RFID in Action: Real-World Applications That Will Blow Your Mind
RFID technology isn’t just a futuristic concept; it’s already transforming industries across the globe:
- Retail: From inventory management to loss prevention, RFID is helping retailers streamline operations and boost their bottom line. Macy’s, for example, reported a 50% reduction in out-of-stocks after implementing RFID.
- Healthcare: RFID is being used to track medical equipment, monitor patient vital signs, and even prevent medication errors. A study published in the Journal of Medical Systems found that RFID reduced medication errors by 51%.
- Logistics: From tracking shipments to managing warehouse inventory, RFID is revolutionizing the way goods move around the world. DHL estimates that RFID has saved them over $1 billion in operational costs.
- Manufacturing: RFID is used to track work-in-progress, monitor equipment performance, and improve quality control. Boeing reported a 30% reduction in production time for its 787 Dreamliner aircraft after implementing RFID.
- Agriculture: RFID is used to track livestock, monitor crop health, and optimize irrigation systems. A study published in the Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research found that RFID improved irrigation efficiency by 20%.
- Security and Access Control: RFID cards or tags are widely used for access control in offices, warehouses, and secure facilities. They provide a reliable way to monitor entry and exit points while generating audit trails for compliance.
With such diverse applications across industries, let’s explore why RFID technology is becoming a must-have for businesses looking to stay competitive.
Why Your Business Needs RFID Technology
RFID technology offers numerous advantages that make it a game-changer for businesses across industries. Here’s why your business should consider adopting RFID:
- Increased Efficiency: RFID automates time-consuming tasks like inventory counts, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic activities.
- Real-Time Insights: With RFID, you can track assets, shipments, or inventory in real-time, enabling better decision-making and proactive management.
- Enhanced Security: RFID tags help prevent theft by tracking high-value items and controlling access to restricted areas.
- Cost Savings: By reducing errors, operational delays, and labor costs, RFID delivers significant ROI over time.
- Scalability: Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, RFID systems can be tailored to meet your specific needs and grow alongside your operations.
- Improved Customer Experience: In retail, RFID speeds up checkout processes, ensures product availability, and enhances personalization through data insights.
Adopting RFID technology isn’t just about keeping up with trends—it’s about staying ahead of the competition by leveraging smarter, more efficient solutions.
The Future of RFID: Buckle Up, It’s Going to Be a Wild Ride
RFID technology is constantly evolving, with new innovations and applications emerging every day. From smart cities to wearable devices, the possibilities are endless.
- Expert Prediction: The global RFID market is expected to reach a staggering $15.2 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 11.3%. That’s like watching your savings account grow exponentially but with technology instead of money!
So, the next time you tap your card to pay for your morning coffee or breeze through a toll booth without stopping, remember the incredible power of RFID technology – the silent force that’s making our lives easier, safer, and more efficient.
What Are the Challenges of using RFID?
To keep track of things, RFID uses tiny computer chips called tags. A reader reads these tags, which can be placed on toys, clothes, or pets. This technology can be useful, but there are some challenges you have to deal with.
- Using radio frequencies: One challenge is that these systems rely on radio frequencies. This signal can be affected by other devices that use the same frequencies. As a result, you can find it hard to read the labels or send the information on them because of this.
- Options for privacy: It is also controversial for privacy reasons. Some people may be concerned about this technology tracking and monitoring them.
- Expense factors: It can also become challenging to set up and maintain RFID systems as well as troubleshoot them when something goes wrong due to the high cost of RFID tags and readers.
- Fear of being hacked: It’s also hard to keep sensitive information safe with an RFID tag since it can be read from a distance.
- Weather issue: RF tags and readers are sensitive to humidity, rain, and extreme temperatures, which can affect their performance.
It can be hard to implement RFID technology, but understanding these challenges can help you prepare.
security and privacy concerns about using RFID
Using RFID, you can track things like toys, clothes, and pets, but there’s a concern about privacy and security. Some people don’t want people to know where they are or what they have. It’s also important to keep RFID information private and secure so that people don’t see it. Here’s what to do:
Keep the information secret
Like a secret code, the information on an RFID tag can be made private using special math called encryption. It makes it hard for people not supposed to see the data to understand it.
Only let the right people see it
RFID data is only accessible by people who have permission to see it. To get to it, they need special tools like fingerprints or passwords.
Please keep it safe from bad guys
To keep out invaders, RFID systems need security measures to keep them from unauthorized access.
Protect the RFID machines
Keeping RFID readers in a secure location and sealing them so no one can open them is a good idea.
Give people a choice
An RFID tag should give people the option to opt out. To be sure, you can do this by allowing them to remove or deactivate the RFID tag or by giving them the option not to have the RFID tag placed on their possessions.
Thus, organizations can help keep RFID tags private and secure by following these steps.
Make Sure you know the RFID standards
Here are a few RFID standards you can check out:
ISO/IEC 18000
RFID standards define the frequencies and protocols the RFID tag and readers should use to communicate.
EPCglobal
It is a set of standards for RFID in supply chain management. Additionally, it defines how You should use RFID tags to track items as they move through the supply chain, from manufacturing to retail.
NFC
This is a standard for short-range wireless communication. Uniquely, the communication between devices used in contactless payments and access control.
RAIN RFID
RAIN RFID stands for UHF RFID. To explain, UHF RFID means ultra-high-frequency radio frequency identification. In brief, it is a standard for RFID in retail and supply chain management. It defines how to use RFID tags and readers to track items at a distance.
Next-generation RFID use
Next-generation RFID is different from normal RFID because people can use it in more ways and do more things. Here are a few examples of how you can use it:
Finding things
Next-generation RFID can find where things are, like people, toys, or even your pet! It can also help people find something they need, like a big store or a warehouse.
Connecting things
Next-generation RFID can connect things to the internet, so people can see information about them and control them from afar. You can use this to improve things like traffic lights or elevators.
Keeping track of things
Next-generation RFID can keep track of things like tools, equipment, or even food! It can help people figure out what they need more of or what’s faulty.
Making cities and transportation better
Urban areas and public transport can use next-generation RFID to make traffic and public services better. It can make it easier for people to get around and make the city a more excellent place.
Overall, next-generation RFID is a way to use technology to make things work better and make our lives easier.
Summing Up
In simple terms, RFID is a way to use small computer chips called tags to keep track of things. You can put these tags on toys, clothes, or your pet’s collar. Special machines called readers can read the information on the labels and tell us where or what the things are.
There are different types of RFID, such as passive, semi-passive, and active RFID. Next-generation RFID is a newer version that can do even more things. You can find items, connect to the internet, and keep track of things. You can also use it to make cities and transportation better.
There are special rules called standards that ensure all RFID tags and readers work together correctly.
However, it’s important to remember that RFID technology has some challenges, such as security and privacy concerns. Therefore, it is crucial to be aware of potential risks and take appropriate measures to protect against them.
RFID is a valuable technology that can make things easier and more efficient.
Ready to take your business to the next level?
Explore how RFID solutions can revolutionize your operations with Tipsoi. Contact us today to learn more about our cutting-edge RFID systems tailored to your industry needs. Let’s build a smarter future together!
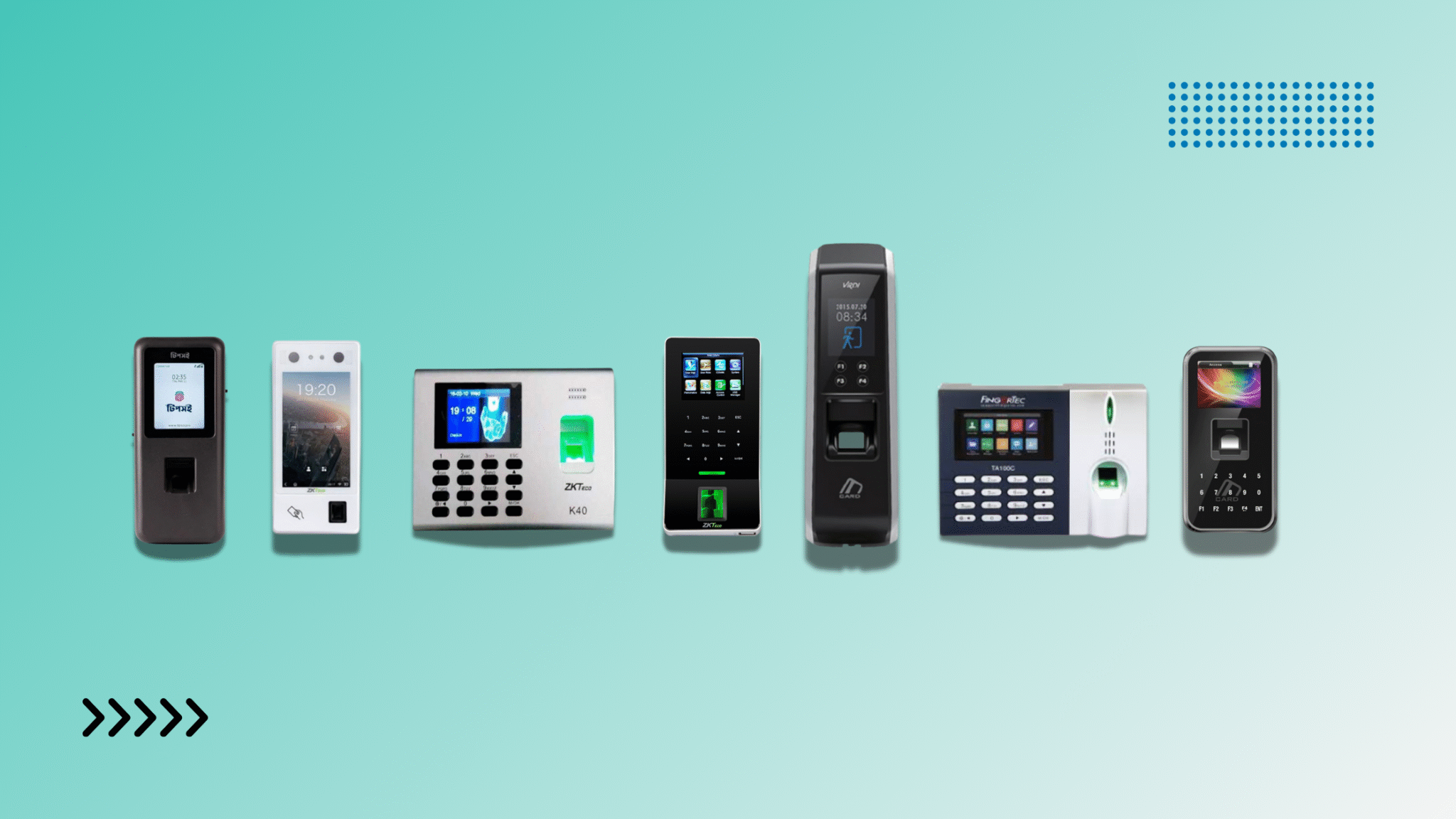
the Best RFID Devices in Bangladesh
Tipsoi
Cloud-Based HR Automation System (Customizable According To Your Need)
➲ All-in-One HR Help:
Fingerprint, RFID, face recognition? Yeah, we’ve got those, all synced up with our web and mobile apps. Attendance, shifts, leave, expenses, payroll, benefits, loans… consider it handled.
➲ World Domination (HR Edition):
Multiple offices? Remote teams? No problem. Our central monitoring puts you in the driver’s seat, giving you real-time insights into your entire workforce, no matter where they are.
➲ Mobile Punch, No Excuses:
Got employees out in the field? Let ’em clock in and out on their phones. We’ll even use Google Maps and a selfie to make sure they’re not sneaking off for a beach day. Our mobile punch feature, complete with GPS and image verification, gives your employees the freedom and flexibility they crave, while still ensuring accountability.
➲ Shift Management: Perfected
Create and manage shifts with a few clicks. No more schedule conflicts, no more confusion. Just pure, streamlined efficiency. With Tipsoi it’s easy to set up and monitor different work shifts and make sure people are working when they’re supposed to.
➲ Employee Data: Organized, Accessible, & (Dare We Say) Enjoyable:
No more digging through piles of paperwork. All your employee information is stored securely in the cloud, accessible anytime, anywhere. It’s like having your own personal HR assistant, always at your service.
➲ Versatility and Scalability:
From Fortune 500 companies to local startups, Tipsoi’s got the flexibility to handle it all. We scale with you, adapt to your needs, and empower your HR team to conquer any challenge. Whether you’re a small startup or a global enterprise, Tipsoi is designed to grow and adapt with you. We’re flexible, scalable, and always ready to support your unique HR needs. Global giants, local schools, everyone’s using Tipsoi. We’re adaptable, scalable, and ready to take on your HR challenges.

Biometric Authentication Device by Tipsoi
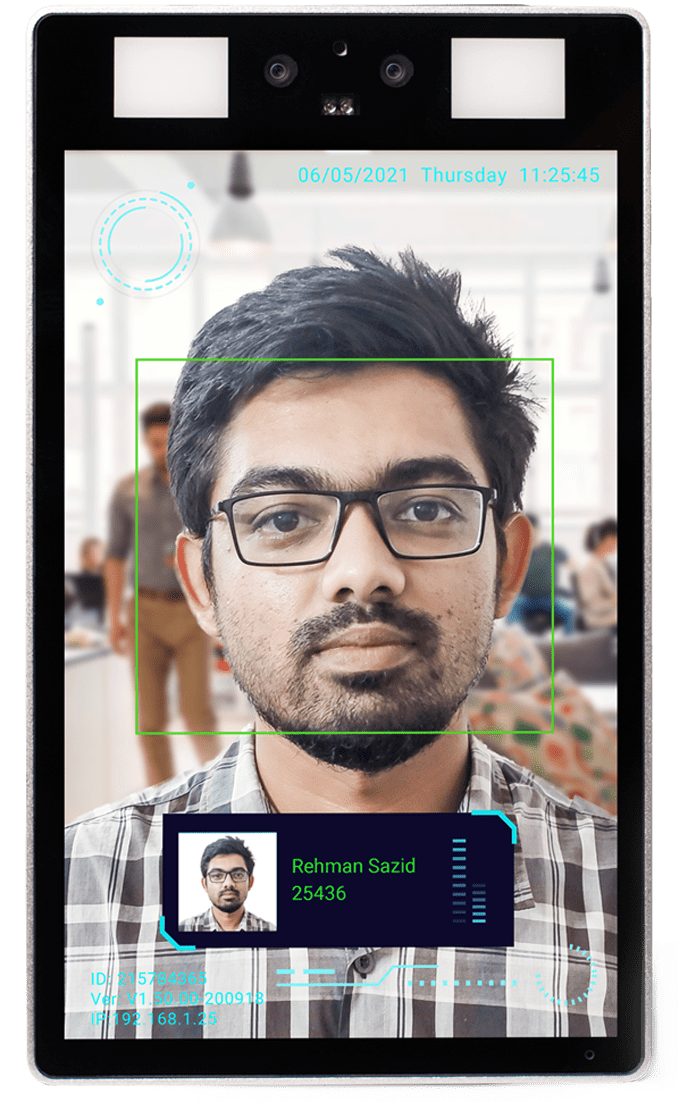
Tipsoi Fastface
Smart Attendance Solution
Inovace Technologies has introduced Tipsoi Fastface, an intelligent
Facial recognition-based device has four different options for you to choose from:
Tipsoi is a cloud-based HR platform that can be accessed from anywhere in the world. It is also customizable and affordable.
Here are some additional benefits of using Tipsoi:
- Improved security: Tipsoi uses state-of-the-art security measures to protect your data.
- Increased efficiency: Tipsoi can help you automate many HR tasks, saving you time and money.
- Improved accuracy: Tipsoi can help you track employee attendance and other data more accurately.
- Better reporting: Tipsoi can help you generate reports on employee activity, which can help you make better decisions about your workforce.
The Bottom Line: Tipsoi is the HR tech you didn’t know you needed (but definitely do). We’re the solution you’ve been waiting for – powerful, intuitive, and ready to take your HR game to the next level.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Still have questions about how RFID works or whether it’s right for your business? Here are answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about RFID technology.
What is RFID, and how does it work?
RFID, or radio frequency identification, uses radio waves to identify and track objects. It works by having a tag with a microchip and antenna that transmits information to a reader.
What are the different types of RFID systems?
The main types are passive, active, and semi-passive. Passive RFID tags don’t have a power source and rely on the reader’s energy, while active RFID tags have a battery and can transmit data independently. Semi-passive tags have a battery to power the microchip but still rely on the reader for transmission.
What are the key benefits of using smart labels in retail?
Smart labels can enhance inventory management, improve supply chain visibility, increase efficiency, improve security, and provide a better customer experience.
What are some common applications of RFID technology?
RFID is used in various applications, including inventory management, access control, asset tracking, supply chain management, animal tracking, and retail.
What are some challenges associated with RFID technology?
Some challenges include potential interference from other radio frequencies, privacy concerns, the cost of implementation and maintenance, and the need for security measures to protect sensitive information.
What is the future of RFID technology?
Next-generation RFID is expected to expand its capabilities beyond simple tracking. It can be used for locating items, connecting devices to the internet, monitoring assets, and improving city infrastructure and transportation systems.
What is RFID technology used for?
RFID is used for tracking and managing assets, inventory, and personnel in industries like retail, healthcare, logistics, manufacturing, and agriculture. It automates processes, improves accuracy, and provides real-time data insights.
How does RFID differ from barcodes?
Unlike barcodes, RFID does not require line-of-sight scanning. RFID tags can be read from a distance, store more data, and are reusable, making them more efficient for large-scale operations.
Is RFID technology expensive?
While initial setup costs may seem high, the long-term benefits—such as reduced labor costs, improved accuracy, and enhanced security—often outweigh the expenses.
Can RFID work in harsh environments?
Yes, RFID tags are designed to withstand extreme conditions like high temperatures, moisture, or dust. This makes them ideal for industries like manufacturing and agriculture.
How secure is RFID technology?
Modern RFID systems use encryption to protect data and prevent unauthorized access. Additionally, access control measures can be implemented to enhance security further.
Can RFID work over long distances?
Active RFID tags can transmit data over several meters, making them ideal for logistics and large-scale operations.
What industries benefit most from RFID?
Industries like retail, logistics, healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation see significant benefits from RFID technology.