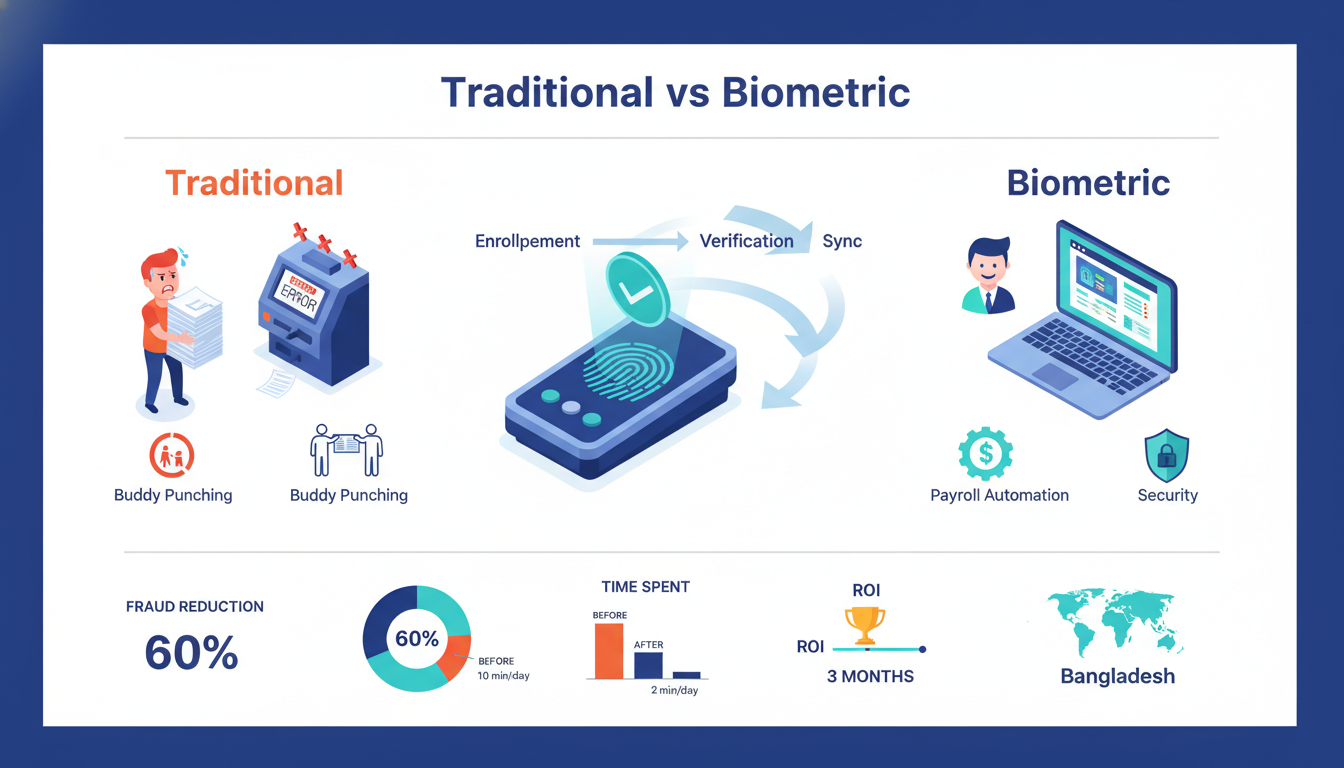
Managing employee attendance is one of the most time-consuming tasks for HR teams in Bangladesh. Traditional punch cards, manual registers, and Excel sheets create endless problems: buddy punching, fake entries, payroll delays, and hours wasted on data entry.
A biometric attendance solution solves these issues by using fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans to verify who’s actually present. These systems eliminate fraud, automate payroll calculations, and give managers real-time visibility into their workforce.
This guide explains how biometric attendance systems work, why they matter for Bangladeshi businesses, and what to consider before implementing one.
What Is a Biometric Attendance System?
A biometric attendance system uses unique physical characteristics to track when employees arrive, leave, and take breaks. Unlike ID cards or passwords, biometric data can’t be shared, stolen, or faked.
The system stores a digital template of each employee’s biometric trait during enrollment. When they clock in, the device scans their fingerprint, face, or iris and compares it against stored templates. If there’s a match, the system records the timestamp and syncs it with HR software.
Most modern biometric systems connect to cloud platforms or local servers. This means managers can view attendance reports from anywhere, approve leave requests instantly, and spot patterns like chronic lateness or unexpected absences.
Why Attendance Tracking Fails in Many Bangladeshi Workplaces
Attendance fraud costs Bangladeshi companies millions in lost productivity each year. The problems start with outdated tracking methods that rely on paper, manual verification, or basic swipe cards.
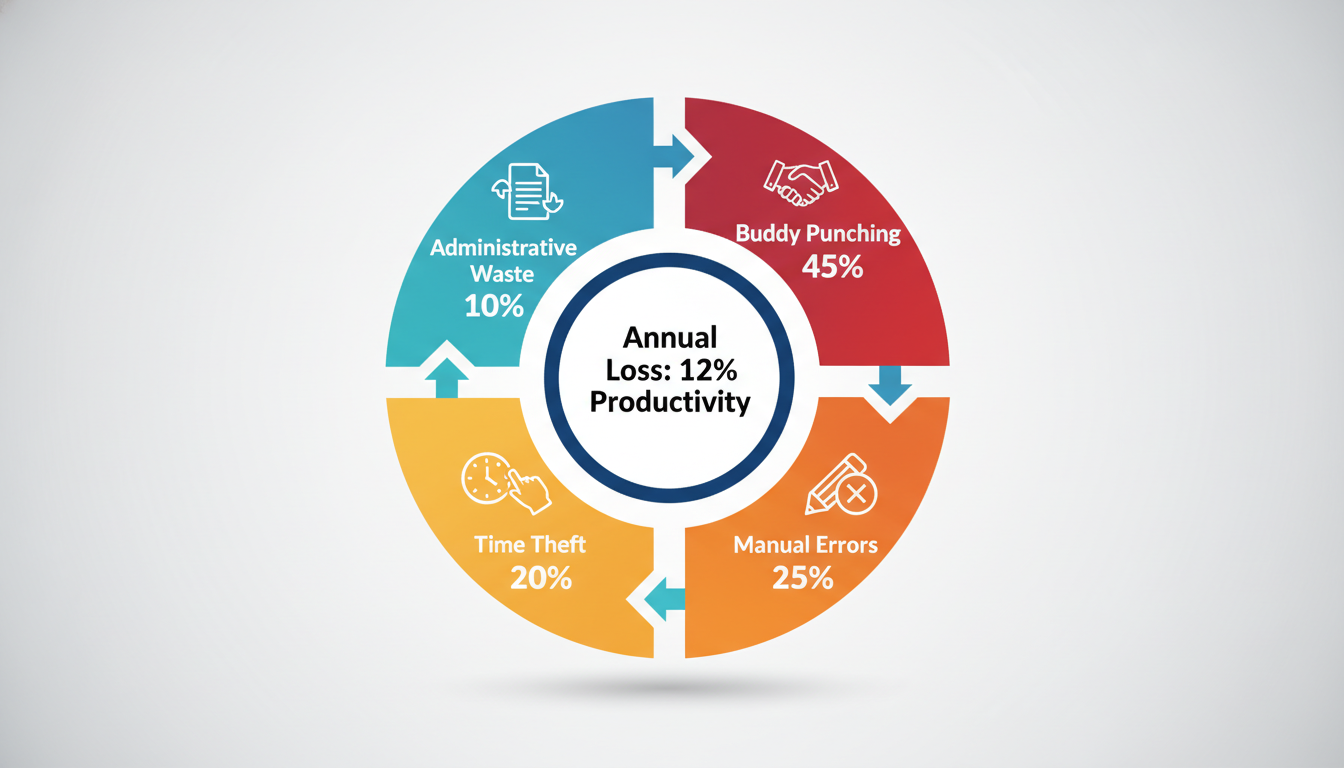
Buddy punching is the most common issue. One employee clocks in for a coworker who’s running late or absent. In factories with hundreds of workers, this happens constantly. A study by the American Payroll Association found that 75% of businesses lose money to buddy punching.
Manual registers create other headaches. Supervisors spend hours reviewing handwritten logs, checking for discrepancies, and fixing errors. When payroll time arrives, HR teams manually count attendance days, calculate overtime, and cross-reference leave records.
Card-based systems fail just as often. Employees forget cards, lend them to colleagues, or lose them entirely. Replacing cards costs money, and verifying that the right person used the card is impossible.
The real cost isn’t just money. It’s the time managers waste investigating attendance disputes, the frustration employees feel when payroll is wrong, and the lack of data needed to plan shifts effectively.
How Biometric Workforce Management Systems Work
Biometric attendance systems follow a three-step process that takes seconds but saves hours of administrative work.
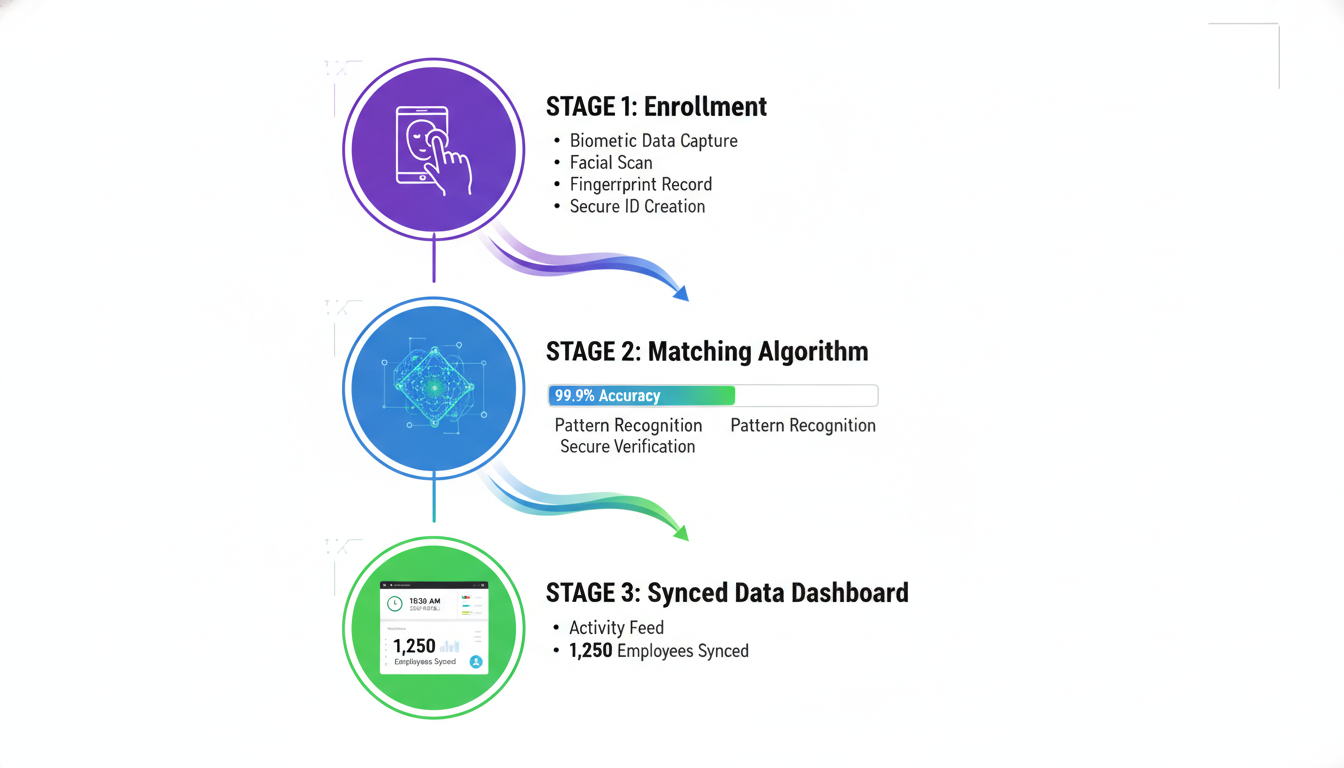
Employee Enrollment
During setup, each employee registers their biometric data. For fingerprint systems, they press their finger on the scanner multiple times. The device captures ridge patterns and converts them into a mathematical template.
Facial recognition systems take photos from different angles. The software maps facial geometry including the distance between eyes, nose shape, and jawline structure.
The important part: systems don’t store actual fingerprints or photos. They store encrypted mathematical representations. This protects privacy because raw biometric data never leaves the device.
Verification
When an employee arrives at work, they interact with the biometric device. Fingerprint readers require placing a finger on the scanner. Facial recognition cameras identify employees as they walk past. Iris scanners use near-infrared cameras to photograph the eye from a short distance.
If verification succeeds, the system records the timestamp, employee ID, and location. Match decisions happen in under one second.
Data Sync
After verification, attendance data syncs with HR software. Cloud-based systems upload records instantly over the internet. Offline systems store data locally and sync when internet becomes available.
The software automatically calculates total hours worked, late arrivals, overtime hours, absent days, and leave balance. This data flows directly into payroll systems, eliminating manual counting entirely.
Ready to upgrade your time tracking? Explore Check out our detailed guide on biometric attendance software including fingerprint, face recognition, and hybrid options built for modern businesses.
Key Benefits of Biometric Attendance Systems for Workforce Management in Bangladesh
Switching to biometric attendance creates immediate improvements across workforce management.
Elimination of Fraud and Manual Errors
Buddy punching becomes impossible. Each employee must physically be present to verify their identity. Manual calculation errors disappear because software counts attendance days perfectly every time.
One Dhaka-based garment factory with 800 workers eliminated 12% of fraudulent clock-ins within the first month of implementing fingerprint scanners.
Automated Payroll Processing
Integration between attendance and payroll systems cuts processing time by 70% or more. HR software imports verified attendance data, applies pay rates, calculates overtime multipliers, and deducts unpaid leave automatically. Errors that caused payment disputes drop to nearly zero.
Enhanced Employee Productivity & Security
Biometric systems create accountability. When employees know attendance is tracked accurately, punctuality improves. Security also improves because only verified employees can access facilities. The system creates an audit trail showing exactly who entered which areas at what times.
Real-Time Attendance Insights
Managers gain visibility they never had before. Dashboard views show current attendance across departments, locations, or shifts. Historical reports reveal patterns like which departments have the highest absenteeism or whether certain shifts are consistently understaffed.
Improved Compliance and Auditing
Bangladesh labor laws require companies to maintain accurate attendance records. Biometric systems create tamper-proof logs with timestamps and biometric verification. During inspections or audits, you can instantly produce comprehensive reports showing employee work hours, overtime, and leave history.
Streamlined HR Operations
HR teams shift from data entry to strategic work. Leave management becomes simpler because employees request leave through the system and managers approve with one click. Report generation that took days now takes minutes.
Supports Workforce Planning
Accurate historical data helps predict future needs. Attendance patterns combined with productivity metrics help determine if you’re understaffed, overstaffed, or properly balanced.
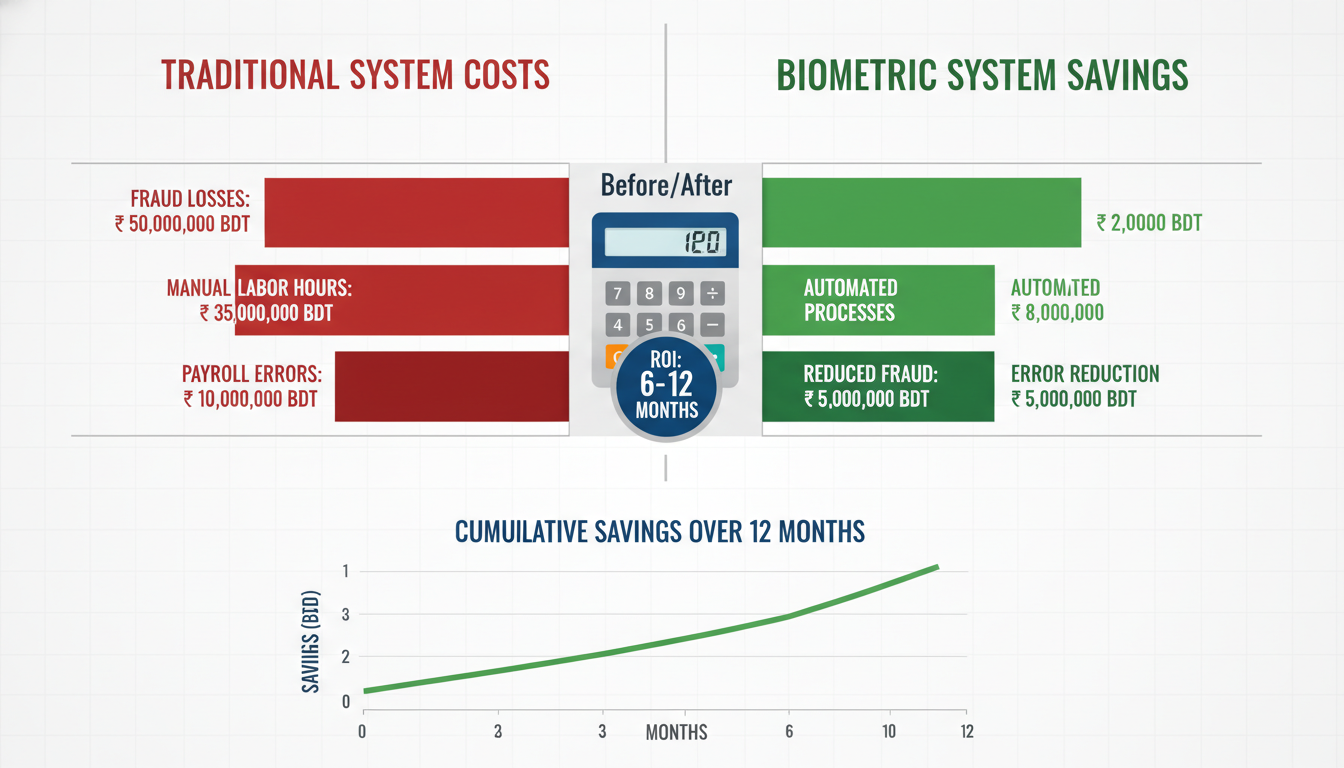
Reduces Costs
The direct savings add up quickly by eliminating buddy punching, reducing payroll processing labor costs, and lowering expenses from manual errors. Most companies see ROI within 6-12 months.
Support for Hybrid and Remote Work
Modern biometric systems work beyond physical offices. Mobile apps with facial recognition let remote workers clock in from home. Field staff use smartphone apps to check in at client sites with GPS verification confirming their location.
Key Biometric Attendance Modalities Used in Bangladesh (2026)
Different biometric technologies suit different workplace needs.
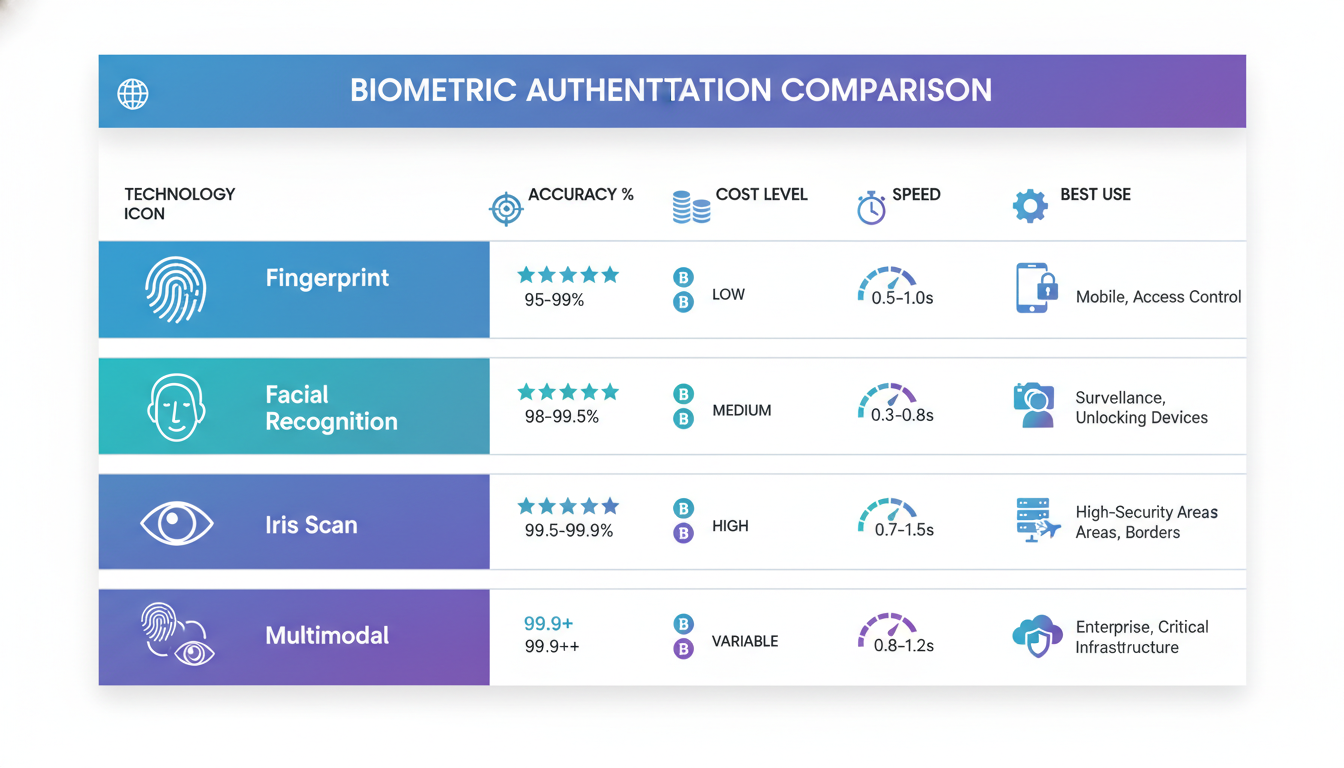
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition cameras identify employees without physical contact. Workers simply walk past the device. The technology maps facial features into a unique mathematical signature and works well even with glasses or masks.
Best for: Offices, retail locations, hospitals, and any environment prioritizing hygiene and speed.
Fingerprint Scanning
Fingerprint readers are the most common biometric modality in Bangladesh. Employees press their finger against a sensor for 1-2 seconds. Match accuracy exceeds 99.9% when properly maintained. Devices are affordable, compact, and work offline.
Best for: Factories, warehouses, small offices, and budget-conscious implementations.
Iris Scanning
Iris recognition uses infrared cameras to photograph the unique pattern in the colored ring of your eye. It’s the most accurate biometric technology available but costs more than fingerprint or facial systems.
Best for: High-security environments like pharmaceutical labs, data centers, or research facilities.
Multimodal
Multimodal systems combine two or more biometric types like fingerprint plus facial recognition. This provides higher accuracy and better handling of edge cases.
Best for: Banks, government facilities, and organizations with strict security requirements.
Biometric Attendance Use Cases by Industry
Different industries face unique workforce challenges.
Garments and Factory Shift Teams
Bangladesh’s garment sector employs over 4 million workers across multiple shifts. Biometric systems verify hundreds of workers entering and leaving during shift changes, link each worker to their piece-rate production output with perfect accuracy, and generate compliance documentation showing exact work hours for export buyers.
Retail and Multi-Branch Offices
Retail chains struggle to monitor attendance centrally across stores. Biometric solutions provide centralized visibility so head office managers see real-time attendance across all locations. They also track staff rotation between branches and link point-of-sale data with attendance for loss prevention.
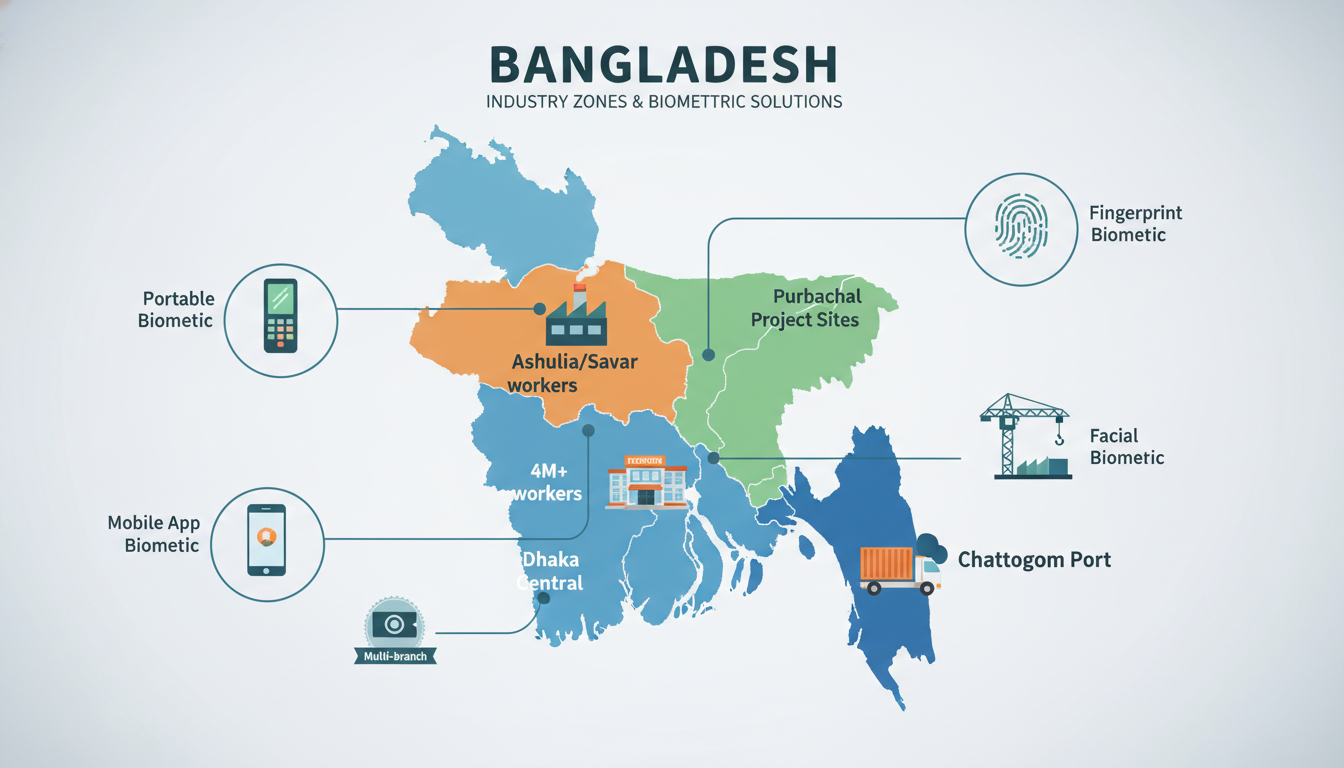
Logistics, Warehouses, and Field Staff
Logistics companies manage scattered workers across different locations. Fingerprint devices at warehouse loading docks track shifts precisely. Delivery drivers use mobile apps with facial recognition to clock in from client locations with GPS stamps confirming correct delivery points.
Construction and Project Sites
Construction sites are temporary and often lack reliable internet. Portable fingerprint readers with local storage work without internet and sync later. The system distinguishes between company employees and subcontracted workers for accurate billing. Biometric entry logs also prove who was on-site during safety incidents.
Implementation Considerations for Biometric Attendance Systems
Successful implementation requires planning beyond just buying devices.
Data Privacy
Biometric data is sensitive. Choose systems that encrypt biometric templates both in storage and during transmission. Inform employees clearly about what biometric data you collect, how it’s used, and who can access it. Only collect data necessary for attendance tracking, and define how long you keep biometric records after employees leave.
Connectivity
Bangladesh’s internet infrastructure remains inconsistent outside major cities. Choose systems that operate both online and offline. Devices should cache attendance data locally and sync when internet becomes available. Consider systems with multiple connection options like Wi-Fi, ethernet, and mobile data.
Offline Functionality
Complete offline operation is essential for many Bangladeshi businesses. Devices need enough memory to store several days of attendance records. The biometric reader should verify employees against stored templates without contacting a server, ensuring instant verification even offline.
Compliance
Your biometric system should flag when employees approach legal maximum working hours, track mandatory break times, calculate overtime at correct premium rates, and maintain attendance records for legally required periods. Every attendance modification should create an audit log showing who made changes and when.
Why Tipsoi Is a Strong Biometric Attendance Solution for Bangladeshi Businesses ?
Tipsoi offers a comprehensive biometric attendance platform designed specifically for Bangladesh’s business environment. The system handles unreliable connectivity, diverse workforce types, and the need for affordable yet reliable technology.
Flexible deployment options mean Tipsoi works in modern Dhaka offices and remote factory locations. Multiple biometric modalities give businesses choice between fingerprint readers, facial recognition, or multimodal systems. Mobile workforce support extends to field staff and remote workers using the Tipsoi app with facial recognition and GPS verification.
Payroll integration eliminates double data entry by connecting directly with popular payroll systems. Local support in Bengali and English ensures technical issues get resolved quickly. The platform scales from 10 employees to thousands of workers across multiple locations.
Explore Biometric Attendance Solutions-
Want to know more about different biometric technologies and how to compare? Check out our collection of biometric attendance systems to understand which solution fits your specific workplace needs.
FAQ
What is the most accurate biometric attendance system?
Iris recognition is the most accurate biometric technology, with error rates below 1 in 1 million. However, fingerprint and facial recognition systems offer accuracy above 99.9%, which is more than sufficient for attendance tracking. Most businesses choose based on cost, convenience, and employee comfort.
Can biometric attendance systems work without internet?
Yes, quality biometric systems include offline functionality. Devices store biometric templates locally and verify employees without internet. Attendance records save in device memory and automatically sync when connectivity returns.
Is biometric data safe and private?
When properly implemented, biometric systems are secure. They store encrypted mathematical templates, not actual fingerprints or photos. Choose vendors who encrypt data, limit access to authorized personnel, and comply with data protection standards.
How much does a biometric attendance system cost in Bangladesh?
Basic fingerprint systems start around BDT 15,000-25,000 per device. Facial recognition systems range from BDT 30,000-60,000. Cloud software subscriptions typically cost BDT 50-200 per employee monthly. Most businesses see ROI within 6-12 months.
What happens if an employee’s biometric data doesn’t scan properly?
Modern systems include backup verification methods. If a fingerprint doesn’t scan, employees can use alternative fingers, facial recognition, or PIN codes as fallback. Administrators can also manually mark attendance while maintaining audit trails.