If you want your business to grow and keep your customers happy, you will need to know how important it is to help customers along their journey. It’s not enough to know “why” and “how” to map the customer journey; you also need to choose the right tools and styles. For that reason, this guide is all about the different customer journey mapping tools & templates that can make mapping easier for you. Also, it will help you make customer journey maps that look good and are full of useful information.
Customer Journey Mapping Tools: To Visualize Data
Like a builder needs a full set of tools, customer journey mapping needs a wide range of tools to work well. In fact, different kinds of tools are needed for each step, from coming up with ideas to visualizing them to analyzing the data. Let’s look at these tools that will help you with journey mapping.
1. Brainstorming and Ideation Powerhouses
- Miro: Your team can use this virtual whiteboard to come up with ideas, learn more about the customer journey, and make rough sketches of these ideas.
- Mural: The mural is a digital workspace for visual collaboration that works a lot like Miro. Likewise, it has templates and tools that are perfect for journey mapping.
2. Visualization and Mapping Virtuosos
- Lucidchart: Using Lucidchart, you can easily make journey maps that look professional and are easy on the eyes by dragging and dropping elements on the screen. What’s more, it lets you make your map come to life with a lot of different layouts and editing tools.
- Smaply: This is the best tool for you if you want to really understand the emotional ups and downs of your customers’ journey. Indeed, it’s great at picturing how customers feel and finding their pain points.
Evidently, with these visualization and mapping tools, you can make customer journey maps that look good and are full of useful information. In addition, this will help you discover more about how the customer feels.
3. Data Integration and Analysis Wizards
- FullStory: Using real customer contacts that you record on your website or app, this tool makes it easy to make accurate journey maps quickly. Moreover, you can see everything your customers do if you put yourself in their shoes. As a result, this makes your work more useful and effective.
- Hotjar: Heatmaps and session records provided by Hotjar, a crucial part of this process, show how customers use your website. Therefore, this knowledge is very helpful for making your journey map.
In short, these customer journey mapping tools & templates for combining and studying data give you a lot of information about how customers really act. In addition, this lets you see where customers are having trouble, come up with ways to make things better, and make decisions based on data to improve the customer process.
4. Collaboration and Sharing Champions
- Figma: This app is great for teams that work best when they can share and edit files at the same time. It makes working together on journey maps easy and makes sure that everyone is on the same page.
- UXPressia: This platform makes journey planning easier with built-in features and by connecting to other tools for a more streamlined process.
Leveraging the right customer journey mapping tools & templates enhances collaboration and sharing among your team.
Remember that the best tool for you will depend on the size, budget, and goals of your team. Don’t be afraid to try different things until you find the right fit.
Key Elements of a Customer Journey Map Template
Every effective customer journey map includes certain essential components. Understanding these elements helps you create maps that provide real insights and drive meaningful improvements.
1.Persona
The persona represents your typical customer. This includes their age, job, goals, challenges, and preferences. Starting with a clear persona keeps your map focused on real people, not imaginary ones.
Your persona should be based on actual customer data, not assumptions. Use surveys, interviews, and analytics to build accurate customer profiles.
2.Stages
Stages are the major phases customers go through when interacting with your business. Common stages include awareness, consideration, purchase, use, and loyalty.
Each business may have different stages depending on what you sell and how customers buy. Define stages that match your specific customer experience.
3.Touchpoints
Touchpoints are every place where customers interact with your brand. This could be your website, social media, email, phone calls, physical store, or customer service.
Identifying all touchpoints shows you the complete picture of how customers experience your brand across different channels.
4.Actions
Actions describe what customers actually do at each stage. For example, they might search on Google, read reviews, compare prices, make a purchase, or contact support.
Documenting these actions helps you understand customer behavior and spot patterns in how people move through their journey.
5.Emotions
Emotions show how customers feel at different points in their journey. Are they excited, confused, frustrated, or satisfied?
Understanding emotions is crucial because feelings drive decisions. When you know where customers feel negative emotions, you can fix those problems.
6.Pain Points
Pain points are the problems, frustrations, or obstacles customers encounter. Maybe your checkout process is confusing, or your customer service wait times are too long.
Identifying pain points is one of the most valuable parts of journey mapping. These are the areas where you can make improvements that really matter to customers.
7.Opportunities
Opportunities are chances to improve the customer experience or add value. Once you identify pain points and understand customer needs, you can spot opportunities to do better.
These opportunities become your roadmap for making changes that increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Common Customer Journey Map Types
Different types of customer journey maps serve different purposes. Choosing the right type depends on what you want to learn and improve. If you want to see real-world applications of these maps, check out these examples of customer journey mapping to get inspired.
It can be scary to start from scratch. That’s when themes come in handy! Think of them as pre-built customer journey mapping tools & templates that you can change to fit your business and the way your customers move through it.
Many people use the following types of templates:
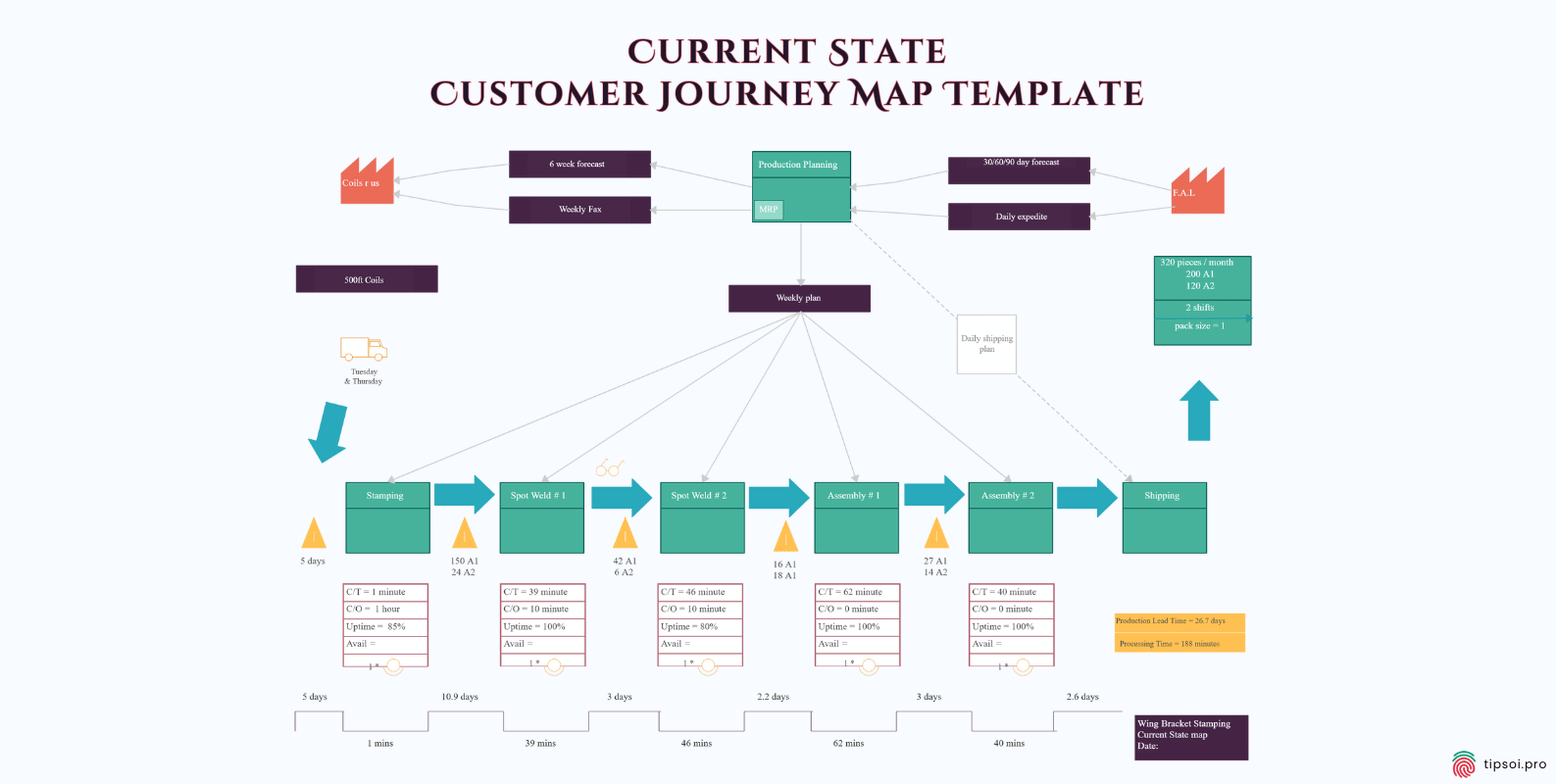
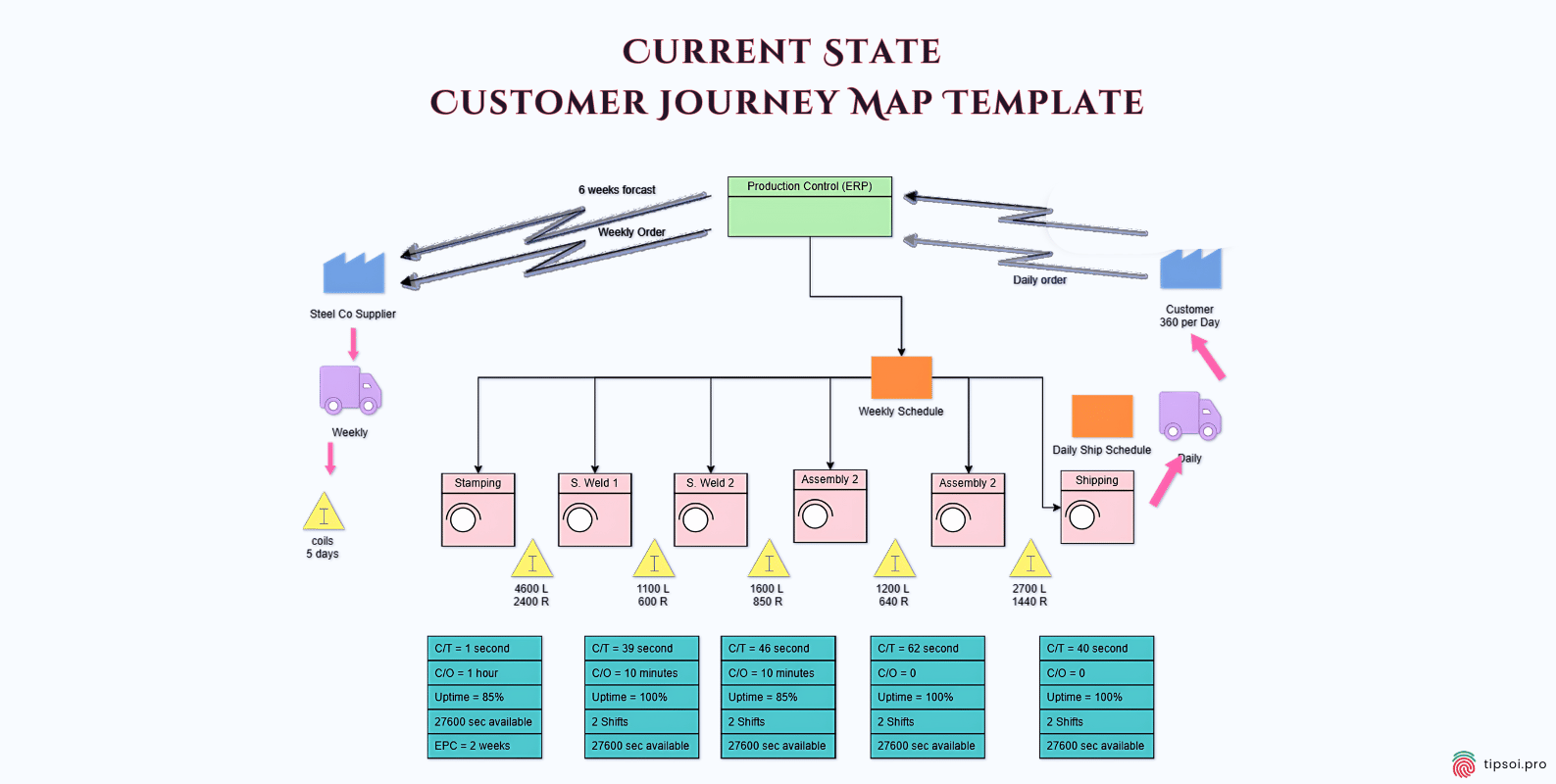
Current State Map Template
A current state map shows how things are right now. It documents the actual customer experience as it exists today, including all the good parts and the problems.
This type of map is most common because it helps you understand reality. You can see what’s working and what needs fixing based on how customers currently experience your brand.
Current state maps use real data from customer feedback, analytics, and observations. They give you a baseline for measuring improvements.
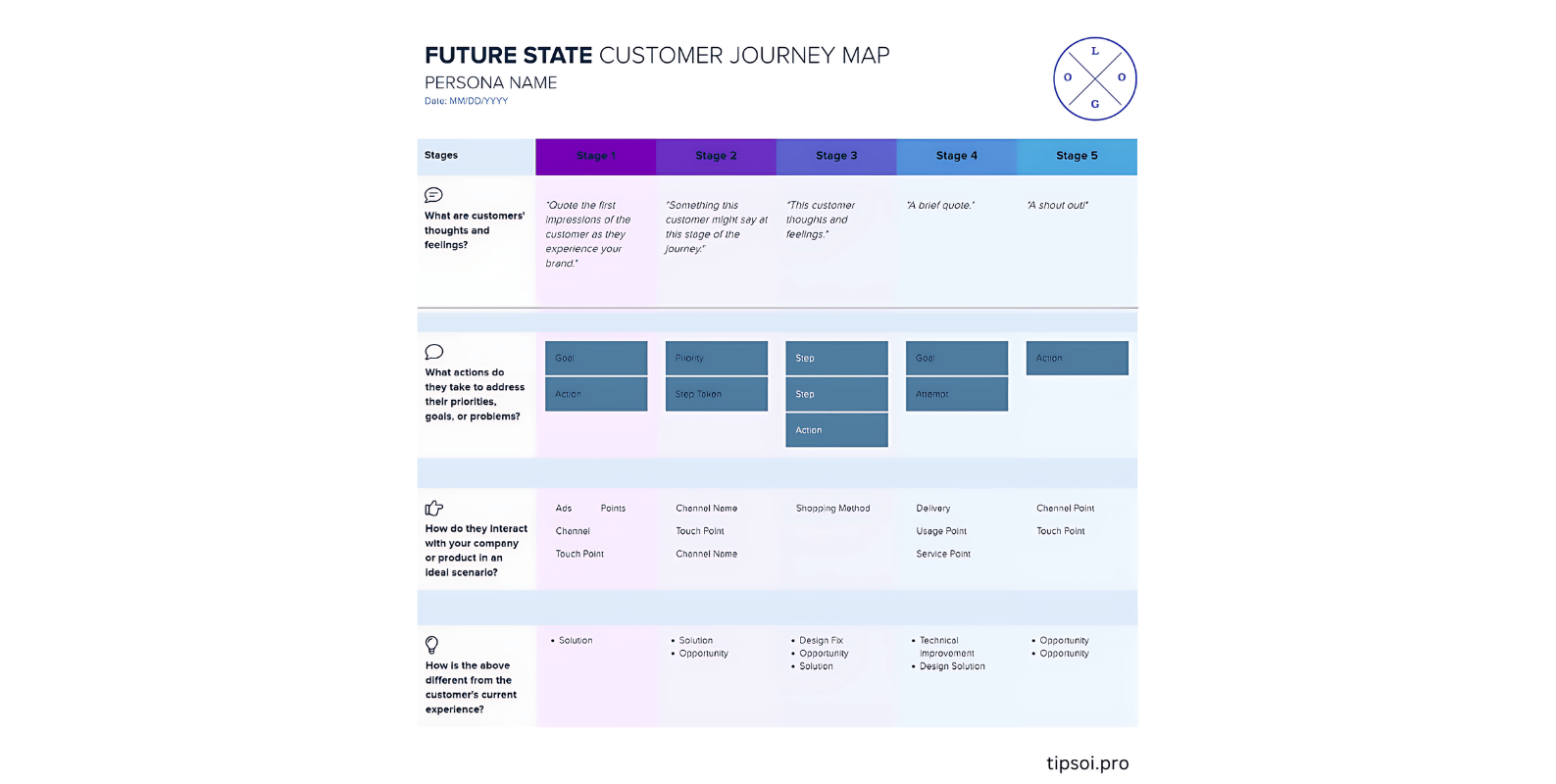
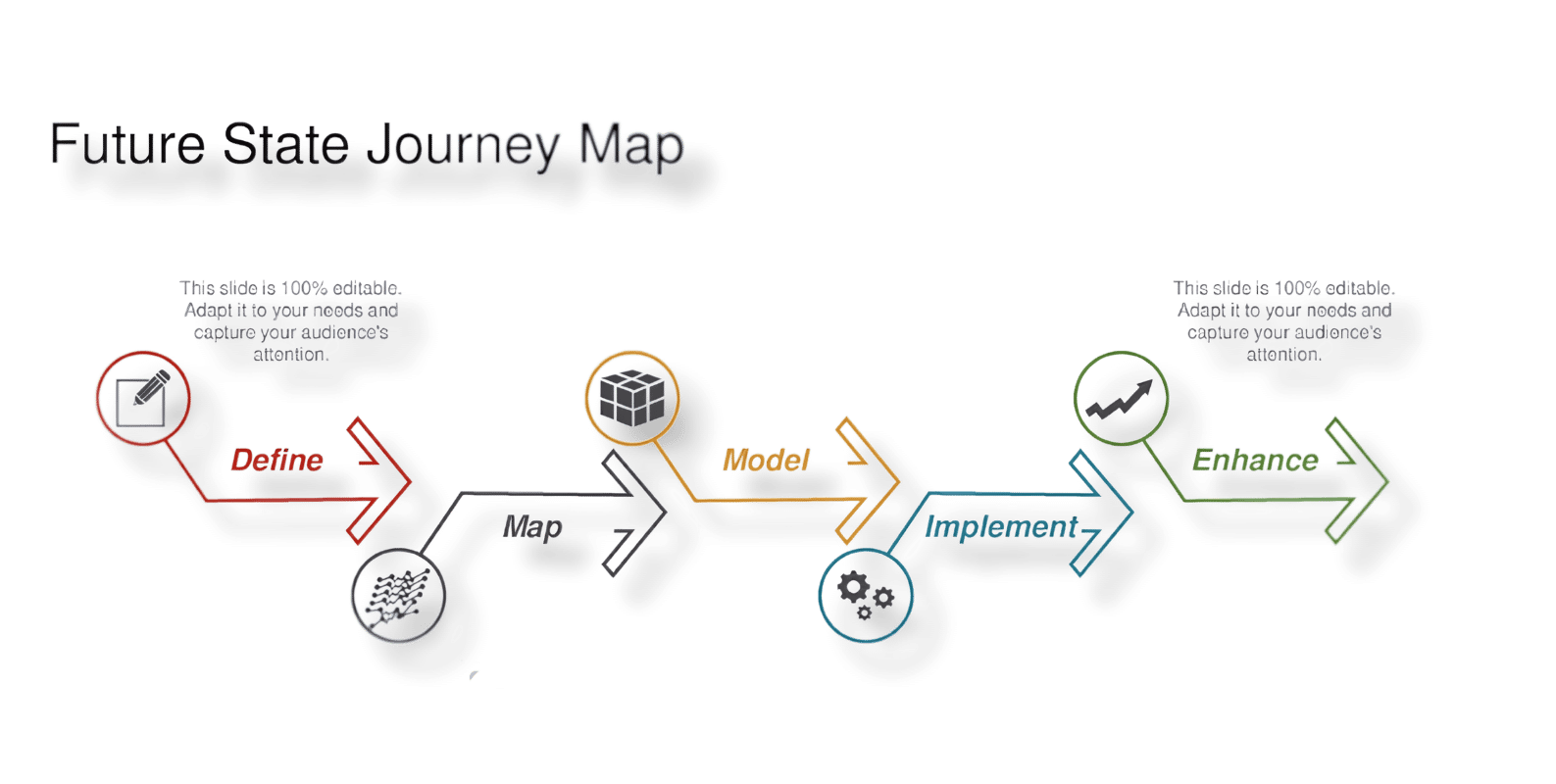
Future State Template
A future state map shows your ideal customer experience. It represents your vision for how things should work after you make improvements.
Creating a future state map helps align your team around goals. It shows what you’re working toward and helps prioritize which changes to make first.
This type of map is aspirational but should still be realistic. Base it on customer needs and what’s actually possible for your business.
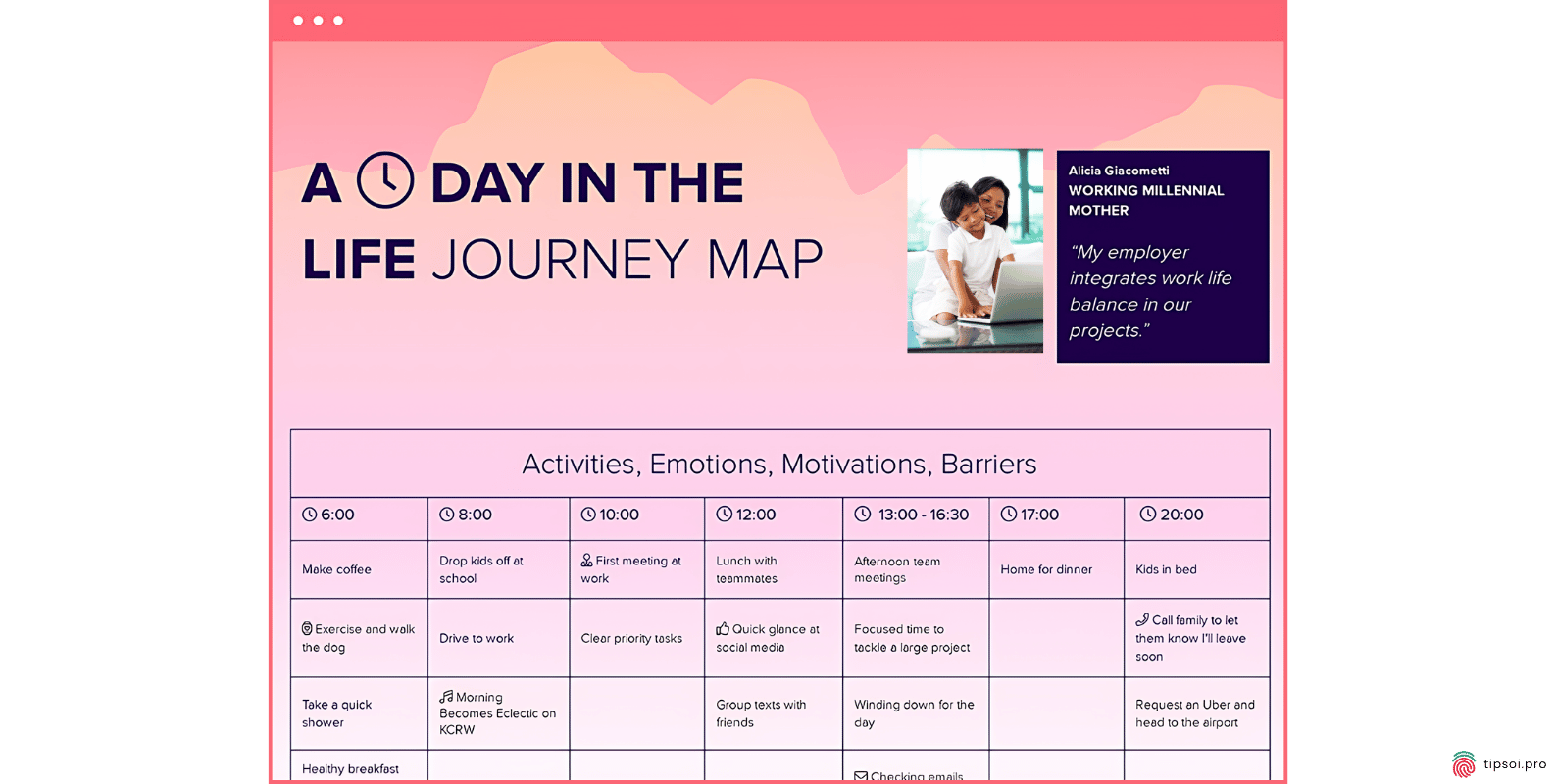
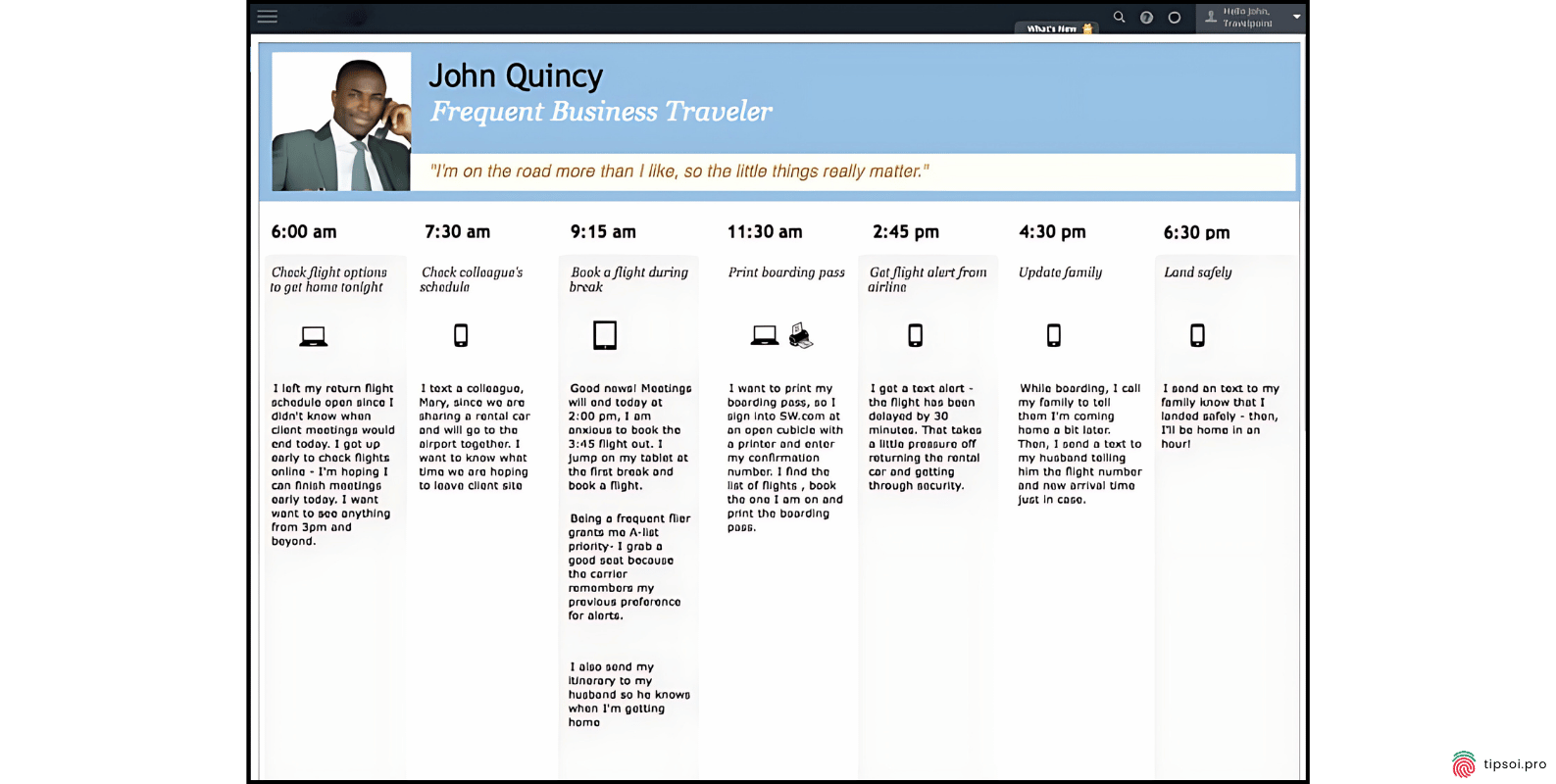
Day in the Life Template
A day in the life map looks at your customer’s entire day, not just their interactions with your brand. It shows what they do, who they talk to, and what challenges they face throughout a typical day.
This broader view helps you understand context. You might discover that customers struggle with your product because of something happening elsewhere in their day.
Day in the life maps often reveal unmet needs and new opportunities that you wouldn’t spot by only looking at direct interactions with your brand.
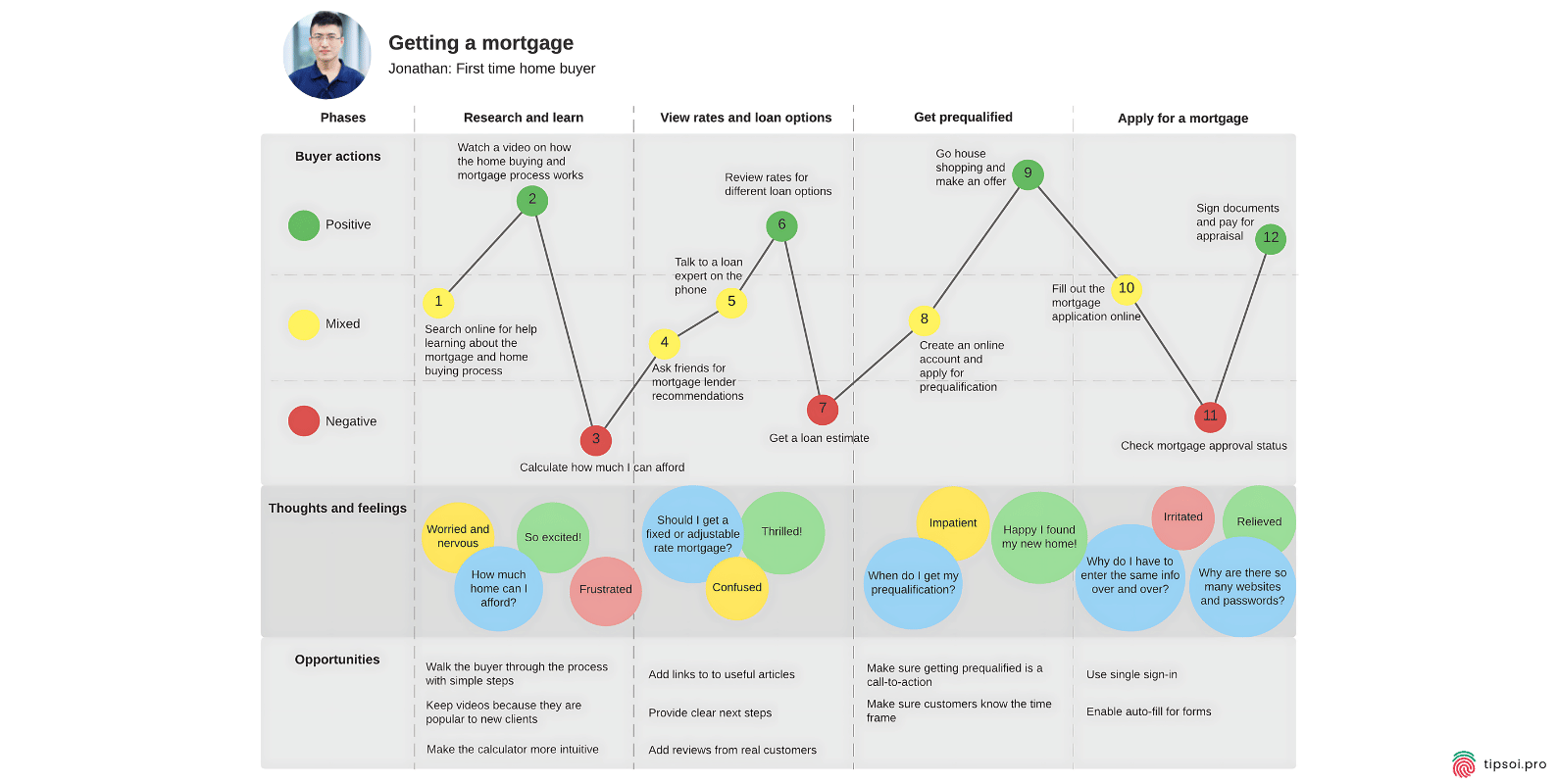
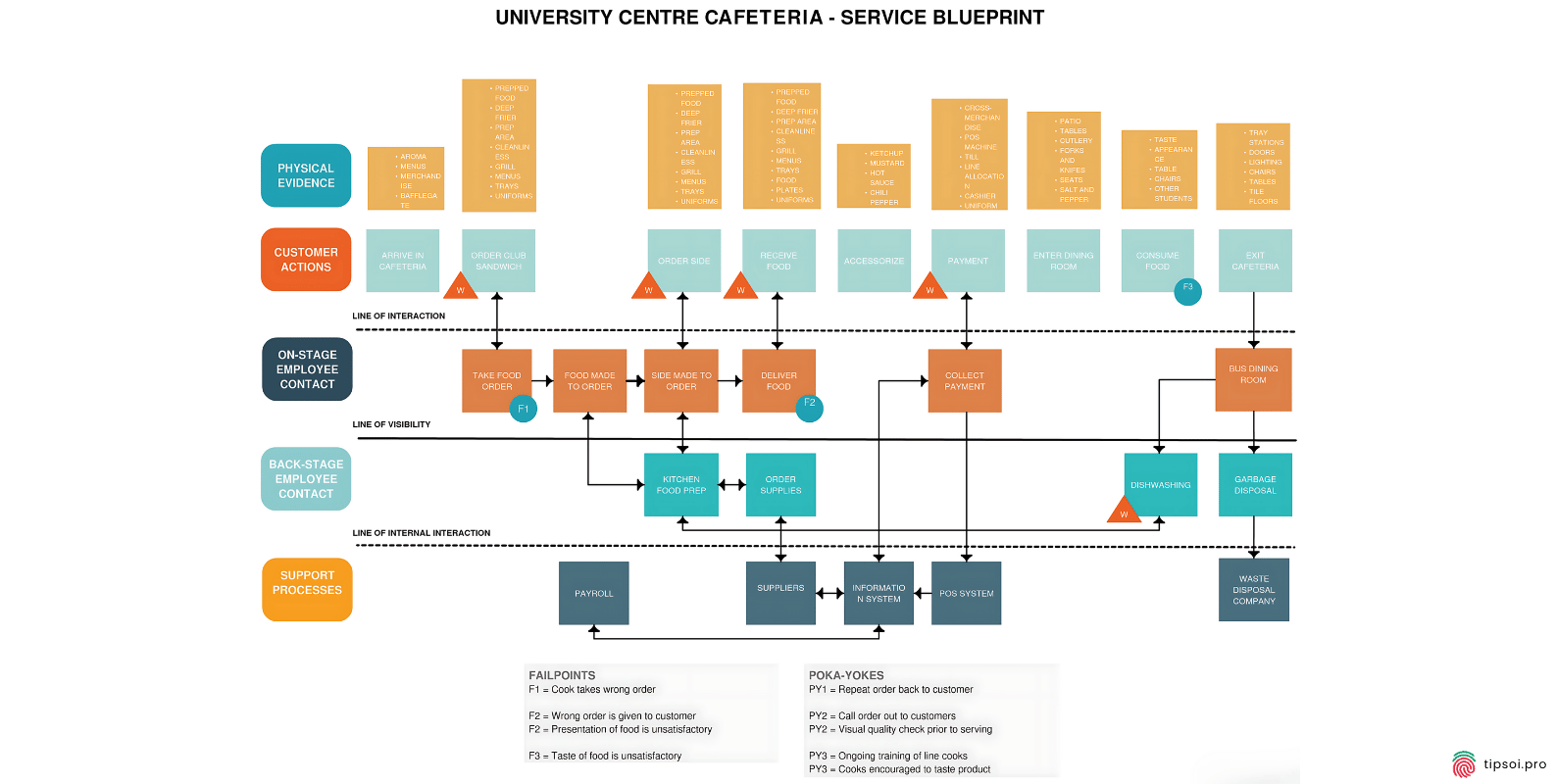
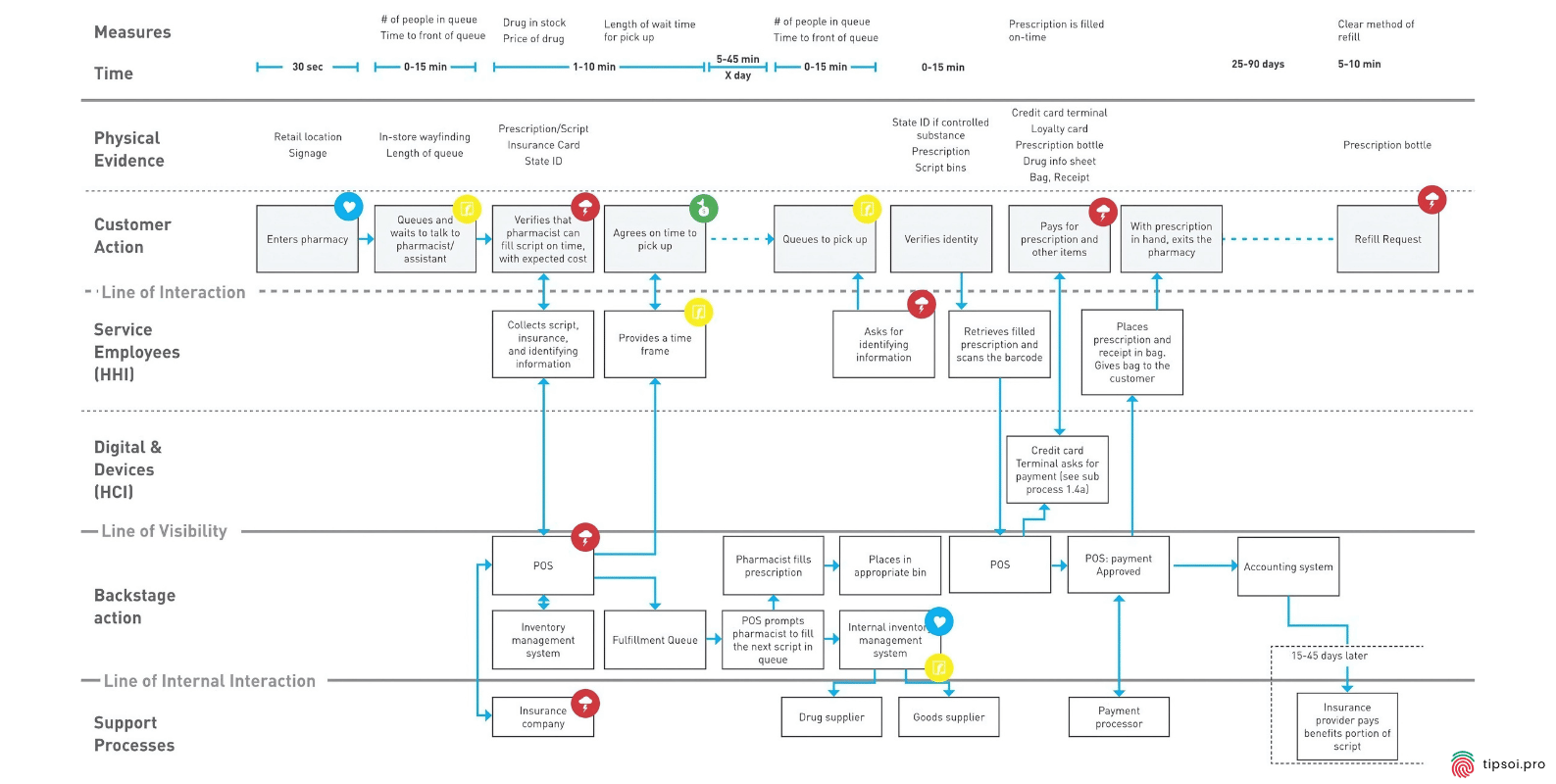
Service Blueprint Template:
This template shows more than just the experience from the customer’s point of view. It also shows the internal processes, people, and tools that are used to make it happen.
Service Blueprint For Getting a Mortgage For The First Time
A service blueprint goes deeper than other maps by showing what happens behind the scenes. It includes not only the customer’s experience but also the internal processes, employees, and systems that make that experience possible.
This type of map helps you understand operational issues. If customers face problems, you can see whether the root cause is a process issue, a staffing problem, or a technology limitation.
Service blueprints are especially useful for complex services that involve multiple departments and systems working together.
AService Blueprint For University Cafeteria
Service Blueprint For A Pharmecy Customer Journey
Pro Tip: Don’t be afraid to mix and match themes or make your own hybrid version that works best for you.
Why Journey Maps Drive Revenue and Trust
Customer journey maps aren’t just nice-to-have documents they directly impact your bottom line and build stronger customer relationships.
When you understand exactly what customers experience, you can fix the problems that make them leave. Studies show that customers who have a smooth, positive experience spend more money and stay loyal longer. They also tell their friends about your business, which brings in new customers without extra marketing costs.
Journey maps help you find the exact moments where customers get frustrated or confused. Maybe your checkout process has too many steps, or your customer service response time is too slow. When you fix these pain points, customers complete purchases instead of abandoning their carts. They come back instead of switching to competitors.
Trust grows when customers feel understood. Journey mapping forces you to see things from their perspective. When you make changes based on what customers actually need—not what you assume they need—they notice. They feel valued. This builds trust that turns one-time buyers into loyal advocates.
From a revenue perspective, journey maps help you spot upsell and cross-sell opportunities. You can see exactly when customers are most engaged and ready to buy more. You can also identify where you’re losing money—maybe customers call support repeatedly about the same confusing feature, costing you time and money.
Journey maps also align your entire team around the customer. When marketing, sales, product, and support all work from the same understanding of the customer experience, you eliminate contradictions and create a consistent brand experience. This consistency builds trust and makes every dollar you spend more effective.
What a Customer Journey Map Includes
A complete customer journey map brings together several key components that work together to tell the full story of your customer’s experience.
Customer persona – This is who you’re mapping for. Include their demographics, goals, frustrations, and what motivates them. A good persona is based on real customer research, not guesses.
Timeline or stages – These are the phases customers go through, like awareness, research, purchase, onboarding, and loyalty. Your specific stages should match how customers actually interact with your business.
Customer actions – What does the customer actually do at each stage? They might search Google, read reviews, visit your website, talk to sales, make a purchase, or contact support.
Touchpoints – Where do these interactions happen? List every channel—website, app, email, phone, social media, physical store, or anywhere else customers meet your brand.
Thoughts and questions – What’s going through the customer’s mind? What questions do they have? What are they trying to accomplish? Understanding their internal dialogue helps you provide better answers.
Emotions – How does the customer feel at each point? Are they excited, anxious, frustrated, confused, or delighted? Emotions drive behavior, so tracking them reveals why customers make certain choices.
Pain points – What problems or obstacles does the customer face? These are friction points that slow them down, cause frustration, or make them consider giving up.
Opportunities – Based on the pain points and customer needs, where can you improve? These are your action items the changes that will make the biggest difference.
Supporting evidence – What data backs up your map? Include quotes from customer interviews, statistics from analytics, support ticket themes, or survey results. Evidence makes your map credible and convincing.
Metrics – How will you measure success at each stage? Define KPIs like conversion rate, time to complete, satisfaction score, or support ticket volume. Metrics help you track whether improvements are working.
When all these elements come together, you get a complete picture that shows not just what customers do, but why they do it and how you can help them succeed.
Tool Setup Checklist Before You Buy
Before you invest in a customer journey mapping tool, work through this checklist to make sure you choose the right solution for your team’s needs.
1.Must-Have Features
Start by listing the features you absolutely cannot work without. These core capabilities should match your specific mapping needs.
Template library – Does the tool offer pre-built templates for different map types? Good templates save time and ensure you don’t miss important elements.
Visual editing – Can you easily drag and drop elements, add images, and customize the look? The interface should be intuitive, even for non-designers.
Real-time collaboration – Can multiple team members work on the same map simultaneously? This is essential if your team works remotely or across different locations.
Export options – Can you download maps as PDFs, images, or presentations? You’ll need to share your maps with stakeholders who don’t use the tool.
Data visualization – Does it include charts, graphs, or emotion curves? Visual data makes patterns easier to spot.
Persona management – Can you create and store multiple customer personas? This helps when mapping different customer segments.
Comments and feedback – Can team members leave notes and suggestions directly on the map? This streamlines the review process.
2.Integrations List
Your journey mapping tool should connect with the other systems you already use. Make a list of your essential tools and check compatibility.
Analytics platforms – Google Analytics, Mixpanel, or Amplitude integration lets you pull real behavioral data into your maps.
CRM systems – Salesforce, HubSpot, or similar tools provide customer information and interaction history.
Survey tools – Qualtrics, SurveyMonkey, or Typeform integration helps you incorporate customer feedback directly.
Project management – Jira, Asana, or Trello connections let you turn pain points into actionable tasks.
Design and collaboration tools – Integration with Slack, Microsoft Teams, or Figma keeps everything connected in your workflow.
Customer support platforms – Zendesk or Intercom integration surfaces common customer issues and questions.
Check whether integrations are native (built-in) or require third-party connectors. Native integrations are usually more reliable and easier to set up.
3.Collaboration Rules
Before rolling out a new tool, establish clear rules about how your team will collaborate on journey maps.
Ownership – Who creates and maintains each map? Assign clear ownership so maps don’t become outdated or inconsistent.
Access levels – Who can view, comment, and edit? Set permissions based on roles to prevent accidental changes while keeping maps accessible.
Naming conventions – How will you name maps and versions? A clear system like “Persona_MapType_Date” helps everyone find what they need.
Review process – How do maps get approved? Define who needs to sign off before a map is considered final.
Update schedule – How often will maps be reviewed and updated? Set quarterly or bi-annual reviews to keep maps current.
Communication protocols – Where will the team discuss maps? Decide whether conversations happen in the tool itself, in Slack, or in meetings.
Version control – How will you track changes over time? Make sure you can see who changed what and when, and roll back if needed.
4.Governance Plan
A governance plan ensures your journey mapping efforts stay organized and valuable over time.
Documentation standards – Create a style guide for how maps should look and what information they must include. Consistency makes maps easier to compare and understand.
Data sources – Define which data sources are approved for informing your maps. Require evidence from customer research, analytics, or feedback—not assumptions.
Archive policy – How long do you keep old maps? Establish when to archive outdated maps versus updating existing ones.
Training requirements – Who needs training on the tool, and what level? Make sure new team members know how to read and contribute to maps.
Quality checks – Who reviews maps for accuracy and completeness? Build in a review step before maps are shared widely.
ROI tracking – How will you measure whether the tool and mapping process are worth the investment? Define success metrics like faster decision-making, improved customer satisfaction, or increased conversion rates.
Stakeholder reporting – How and when will you share maps with leadership? Plan regular presentations that show insights and recommended actions.
Taking time to set up these systems before buying a tool prevents chaos later. You’ll get more value from your investment and build a sustainable journey mapping practice that actually drives improvements.
Tips for Mapping Your Way to Success: Feeling Sure on the Way
Now that you have the tools and templates you need, here are some expert tips to make sure your journey mapping trip goes perfectly:
- Set a clear goal at the start. Figure out what you want your map to do. Are you trying to get more sales, make your customers happier, or something else?
- Include more than one team. The paths that customers take go through many offices. To get a full picture, ask marketing, sales, customer service, and product development for their thoughts.
- Pay attention to how the customer sees things. Think about what they’re going through. At each step of the way, what are their goals, what drives them, and what hurts them?
- Check your assumptions with facts. Don’t go with your gut. Use analytics, polls, and customer feedback to back up what you think.
- Keep it interesting and graphic. A well-made map is simpler to understand and share with others.
- Repeat and get better. Customer trips change over time. Go back to your map often and make changes to reflect how your customers act and your business’s goals.
In the End,
Don’t forget that the point of customer journey planning is to make your organization focus more on the customer. Evidently, by understanding how your customers feel, you can find ways to make their journey better. Additionally, by using the right customer journey mapping tools & templates, you can make this process easier and more effective. This will make them happier, more loyal, and ultimately help your business grow.
Now that you have your tools and template, it’s time to start this exciting journey of learning. Have fun mapping!
FAQs
What are some essential customer journey mapping tools?
There is a range of tools available, including Miro and Mural for brainstorming, Lucidchart and Smaply for visualization, FullStory and Hotjar for data analysis, and Figma and UXPressia for collaboration.
How do I choose the right customer journey mapping tool for my business?
Consider factors like your team’s size, budget, specific needs, and desired features (e.g., real-time collaboration, data integration, emotional mapping) when making your selection.
What are some popular customer journey mapping templates?
Commonly used templates include Current State, Future State, Day in the Life, and Service Blueprint templates, each serving a specific purpose in visualizing the customer experience.
Can I use a combination of customer journey mapping tools and templates?
Absolutely! Feel free to mix and match tools and templates or create your own hybrid version to best suit your needs and preferences.
How can customer journey mapping tools & templates benefit my business?
They streamline the mapping process, enable collaboration, and provide deeper insights into customer behavior, ultimately helping you create a more customer-centric organization.
Are there any free customer journey mapping tools & templates available?
Yes, several tools offer free plans or trials, and numerous free templates can be found online. It’s worth exploring these options, especially for smaller businesses or those just starting with journey mapping