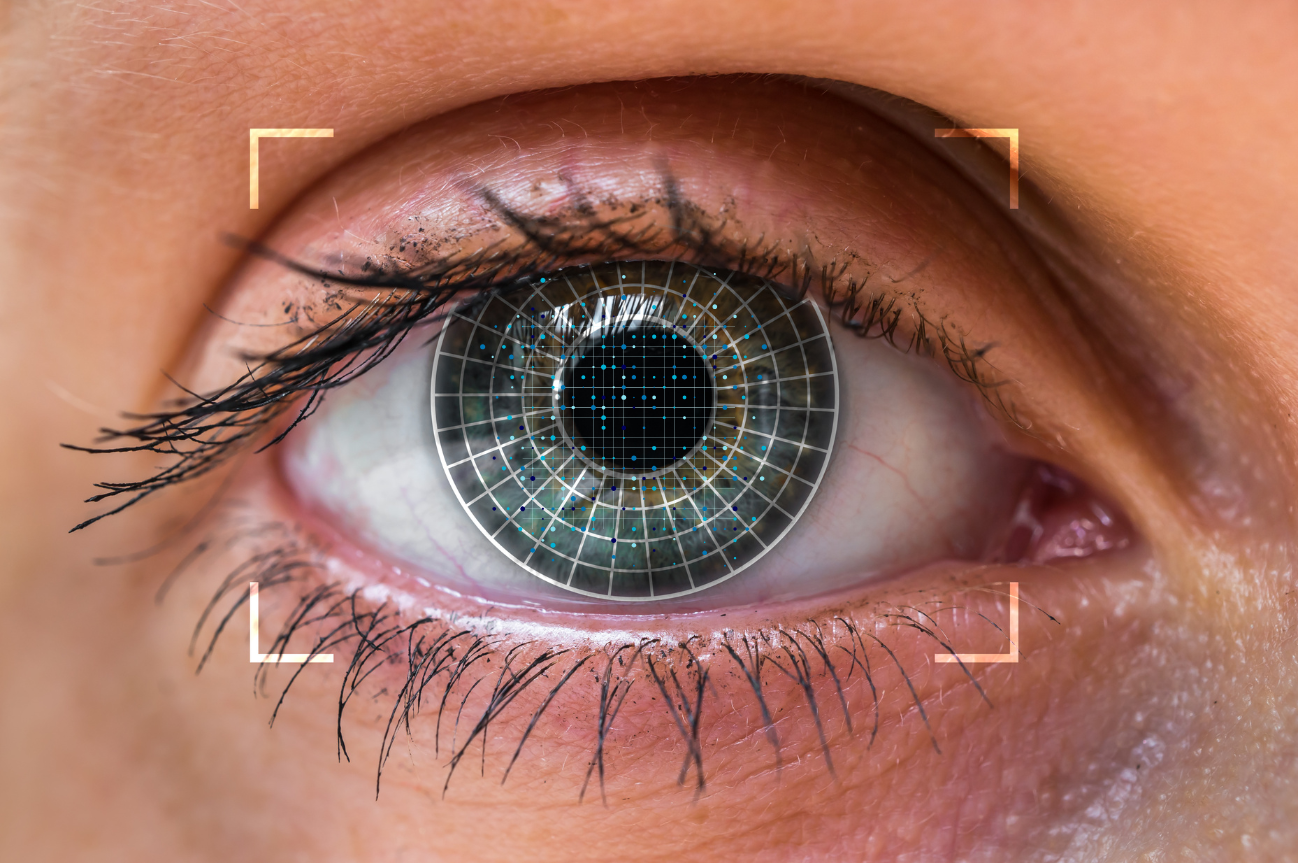
Is iris recognition technology the key to unlocking a more secure future? Absolutely. This complete guide dives deep into the world of iris recognition, an advanced biometric authentication method leveraging the unique patterns within your iris. We’ll explore how it works, its advantages and disadvantages, various applications, and the future of this fascinating technology. Think of your iris as a living, breathing, and incredibly complex fingerprint. With error rates as low as 1 in 1.5 million for a single eye (compared to 1 in 100,000 for fingerprints), iris recognition offers a level of security unparalleled by many other biometric methods. This guide will equip you with everything you need to understand and appreciate the power of iris recognition.
What is Iris Recognition Technology?
Iris recognition is an automated method of biometric identification that uses mathematical pattern-recognition techniques on video images of one or both of the irises of an individual’s eyes. It’s not to be confused with retina scanning, which uses different technology to scan the blood vessel patterns at the back of the eye.
- Biometric Authentication: A process of identifying individuals based on unique biological characteristics.
- Iris Pattern Matching: The core process of comparing a scanned iris pattern against a database of enrolled patterns.
- Ocular Biometrics: A broader category encompassing iris recognition and retina scanning.
How Does Iris Recognition Work? A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The iris recognition process is a multi-stage process that turns the unique patterns of your iris into a secure digital template. Here’s a breakdown:
1. Image Acquisition: A specialized camera, often using near-infrared (NIR) light, captures a high-resolution image of the eye. NIR light is used because it illuminates the iris texture effectively without being intrusive or harmful.
2. Iris Localization: Software algorithms identify the boundaries of the iris, separating it from the pupil and the sclera (the white part of the eye). Accurate localization is crucial for proper analysis.
3. Image Normalization: The identified iris region is transformed into a rectangular block. This “unwrapping” process compensates for pupil dilation, head tilt, and other variations. This normalization step is crucial for accurate comparison.
4. Feature Extraction: Algorithms extract unique features from the normalized iris image. These features include patterns, lines, rings, furrows, and spots. The widely used Daugman algorithm employs Gabor wavelets to analyze the iris texture.
5. Template Generation: The extracted features are converted into a unique digital code, often referred to as an “iris code” or “iris template.” This code represents the individual’s iris pattern.
6. Matching and Verification: During verification, the newly generated iris code is compared against a previously enrolled template stored in a database. A matching score is calculated based on the similarity between the two codes. If the score exceeds a predefined threshold, the individual is authenticated.
The Advantages of Iris Recognition Technology
Iris recognition offers several compelling advantages over other biometric methods:
- High Accuracy: Extremely low false acceptance and false rejection rates. Studies have shown that iris recognition boasts some of the highest accuracy rates among biometric technologies.
- Uniqueness: The iris possesses an incredibly rich and complex texture, making it virtually impossible for two irises to be identical, even in identical twins. Genetic differences account for this variation.
- Stability: The iris pattern is formed early in life (around 8 months of gestation) and remains relatively stable throughout a person’s lifetime. This stability minimizes the need for frequent re-enrollment.
- Non-Invasive: Iris scanning is a non-contact process, reducing the risk of hygiene concerns and increasing user acceptance.
- Spoof-Proofing: Liveness detection techniques can be employed to prevent spoofing attempts using photographs or videos. These techniques often involve analyzing pupil dilation, iris movement, and other physiological responses.
- Speed: The authentication process is generally very fast, often taking only a few seconds.
Disadvantages and Limitations of Iris Recognition
While iris recognition boasts numerous advantages, it also has some limitations:
- Cost: Iris scanners can be more expensive than other biometric devices like fingerprint scanners. This cost can be a barrier to widespread adoption.
- Environmental Factors: Lighting conditions and reflections can sometimes affect the accuracy of the scanning process.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as cataracts or severe eye injuries, can hinder the ability to acquire a clear iris image.
- User Cooperation: While non-contact, users need to position themselves correctly for the scanner to capture a usable image. Lack of cooperation can lead to failed attempts.
- Privacy Concerns: Like any biometric technology, concerns about data security and potential misuse of personal information exist. Strong data protection measures are crucial.
Key Applications of Iris Recognition Technology
Iris recognition technology is finding increasing use in a variety of applications:
- Access Control: Securing buildings, data centers, and other sensitive areas. Iris scanners are used at border crossings and airports to control entry and exit.
- Computer and Network Security: Authenticating users for access to computers, networks, and online accounts. This provides a more secure alternative to passwords.
- Financial Transactions: Verifying identities for banking transactions, ATM withdrawals, and online payments. This helps prevent fraud and identity theft.
- National Identification Programs: Establishing secure and reliable national ID systems. Countries like India (Aadhaar) utilize iris recognition as part of their national identification programs.
- Healthcare: Ensuring patient identification and access to medical records. This helps prevent medical errors and protects patient privacy.
- Law Enforcement: Identifying suspects and victims in criminal investigations. Iris scans can be used to link individuals to crime scenes.
- Mobile Devices: Inclusion in smartphones and tablets for enhanced security and user authentication. More and more high-end mobile devices are incorporating iris scanning capabilities.
- Time and Attendance Systems: Tracking employee attendance and preventing time theft.
Iris Scanner Devices: A Look at the Hardware
Iris scanner devices come in various forms, designed for different applications. Here’s a brief overview:
- Handheld Scanners: Portable devices used for mobile identity verification in law enforcement, border control, and field operations.
- Desktop Scanners: Scanners designed for use in offices, banks, and other fixed locations for access control and authentication.
- Integrated Scanners: Scanners embedded into devices like laptops, smartphones, and ATMs for user authentication.
- Dual-Iris Scanners: Scanners that capture images of both irises simultaneously for enhanced accuracy and security.
These scanners typically use near-infrared (NIR) cameras and sophisticated algorithms to capture and analyze iris patterns. The quality of the camera and the sophistication of the algorithms directly impact the accuracy and reliability of the scanner.
Iris Recognition vs. Other Biometric Technologies
How does iris recognition stack up against other popular biometric methods? Let’s compare:
| Biometric Method | Accuracy | Cost | User Friendliness | Security |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iris Recognition | Very High | High | Moderate | Very High |
| Fingerprint Scanning | High | Low | High | High |
| Facial Recognition | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate | High | Moderate to High |
| Voice Recognition | Moderate | Low | High | Moderate |
| Retina Scanning | Very High | High | Low | Very High |
As you can see, iris recognition offers a compelling combination of high accuracy and security, although it can be more expensive than some other options. While retina scanning offers similar levels of accuracy, it is generally considered more invasive and less user-friendly. Facial recognition is convenient but generally less accurate than iris or fingerprint scanning.
The Future of Iris Recognition Technology
The future of iris recognition technology is promising, with ongoing research and development focused on:
- Improved Accuracy and Speed: Continued advancements in algorithms and hardware are enhancing the accuracy and speed of iris recognition systems.
- Miniaturization and Cost Reduction: Making iris scanners smaller and more affordable to facilitate wider adoption in mobile devices and other consumer electronics.
- Enhanced Liveness Detection: Developing more sophisticated methods to prevent spoofing attempts and ensure the authenticity of iris scans.
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning: Utilizing AI and machine learning to improve the robustness and adaptability of iris recognition systems to various environmental conditions and user demographics.
- Cloud-Based Iris Recognition: Storing and processing iris templates in the cloud for centralized identity management and authentication services.
- Expansion into New Applications: Exploring new applications in areas such as autonomous vehicles, smart homes, and personalized healthcare.
The global iris recognition market is projected to continue growing in the coming years, driven by increasing demand for enhanced security and authentication solutions across various industries.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Iris Recognition
Here are some common questions and answers about iris recognition technology:
1. Is iris recognition the same as retina scanning? No. Iris recognition analyzes the colored part of your eye, while retina scanning analyzes the blood vessel patterns at the back of your eye. They are distinct technologies.
2. Is iris recognition safe? Yes, the technology uses near-infrared light, which is considered safe for the eyes. It’s non-invasive and doesn’t pose any known health risks.
3. Can glasses or contact lenses affect iris recognition accuracy? In some cases, they might. However, modern systems are designed to minimize the impact of glasses and contact lenses.
4. Can my iris pattern change over time? The iris pattern is generally stable throughout a person’s lifetime, but some changes may occur due to aging or certain medical conditions.
5. How secure is iris recognition data? The security of iris recognition data depends on the security measures implemented by the system. Encryption, access controls, and regular security audits are crucial to protect the data from unauthorized access.
6. What happens if my iris scanner is hacked? If an iris scanner is hacked, sensitive data, including iris templates, could be compromised. This highlights the importance of robust security measures and data protection protocols.
7. How much does an iris scanner cost? The cost of an iris scanner varies depending on the type of scanner and its features. Handheld scanners and desktop scanners can range from several hundred to several thousand dollars.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways About Iris Recognition
Iris recognition technology offers a highly accurate and secure method of biometric authentication. Its unique advantages, including its stability, uniqueness, and non-invasive nature, make it a valuable tool for a wide range of applications. While it has some limitations, ongoing research and development are continuously improving its performance and reducing its cost.
Key Takeaways:
- Iris recognition is a biometric authentication method that uses the unique patterns in the iris.
- It boasts very high accuracy rates compared to other biometric methods.
- It’s used in various applications, including access control, computer security, and national ID programs.
- Ongoing research is focused on improving its accuracy, reducing its cost, and expanding its applications.
- While privacy concerns exist, strong data protection measures are crucial for responsible implementation.
As the demand for enhanced security and authentication solutions continues to grow, iris recognition technology is poised to play an increasingly important role in securing our digital and physical worlds. From securing our smartphones to safeguarding our borders, iris recognition offers a glimpse into a future where identity verification is faster, more reliable, and more secure than ever before.
“`