Biometric attendance system solutions verify people using physical or behavioral traits fingerprints, facial patterns or RFID profiles and record time automatically instead of relying on paper timesheets or punch cards. For small businesses, these systems can cut time theft, improve payroll accuracy and simplify HR workflows, but they do require an upfront outlay across devices, software, installation, integration and ongoing support. This guide breaks down the main cost areas to budget for, shows typical price ranges by device type and licensing model, flags common hidden fees, and gives a simple ROI framework to estimate payback.
You’ll find practical examples for fingerprint and facial terminals, a clear comparison of subscription versus perpetual licensing, and line-item figures to help you estimate savings from reduced buddy punching and less administrative work. Keep reading to see how modality, employee count and integration needs shape your total cost and how cloud/IoT features and mobile apps change both one-time and recurring expenses.
What Are the Main Hardware Costs for Biometric Attendance Systems in Small Businesses?
Hardware prices depend on modality, capacity and connectivity: basic fingerprint terminals are the most affordable, facial recognition units with AI cameras sit in the mid-to-high range, and multimodal devices that combine face, fingerprint (Palm Vein Recognition vs Fingerprint……….) and RFID cost more. Key price drivers include maximum user capacity, recognition speed, camera and sensor quality, ruggedness and network options such as Wi‑Fi, Ethernet or cellular IoT. Small businesses should budget beyond the device itself for wall mounts, protective housings, backup power and any extra sensors or RFID badges. Knowing these drivers helps you pick the right device for your headcount and security needs without paying for enterprise features you won’t use.
When comparing hardware, weigh cost against user experience and future maintenance spending a bit more up front can lower support and replacement costs later.
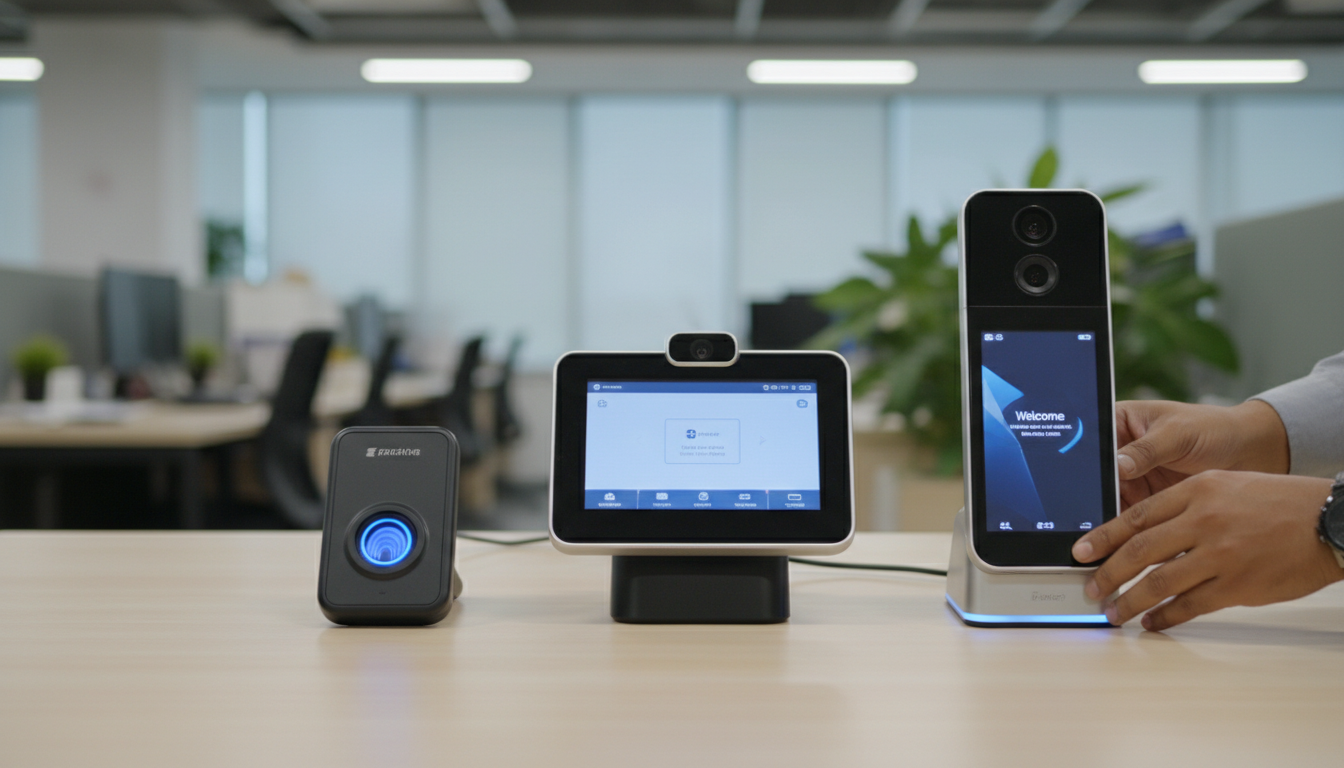

Below is a quick comparison of common device types, their core attributes and representative price bands for small-business deployments.
| Device Type / Model Example | Key Features (Modality, Capacity, Connectivity) | Typical Price Range (representative) |
|---|---|---|
| Entry fingerprint terminal | Fingerprint only, ~500–2,000 users, Ethernet/Wi-Fi | ৳12,000–৳25,000 |
| Facial recognition unit (entry/mid) | Single camera, contactless face, 1,000–5,000 users, cloud-ready | ৳25,000–৳60,000 |
| Multimodal / AI-enabled device | Face + fingerprint + RFID, high accuracy, IoT/cloud, 5,000+ users | ৳60,000–৳100,000 |
The table shows fingerprint devices at the low end and facial/multimodal terminals in the mid to high tiers. The sections below focus on fingerprint and facial pricing in more detail.
How Much Do Fingerprint Time Clocks Cost for Small Offices?
Fingerprint time clocks for small offices start at modest price points and rise with sensor quality, memory and connectivity. Entry models aimed at 10–50 employees typically fall in the lower band and include basic sync options, while more advanced fingerprint terminals add larger template storage, faster matching and cloud sync, moving them into the mid-range. Also expect small accessory costs for wall mounts, protective covers and optional RFID badges or connectors. For small-business owners, match device capacity to your current headcount and choose network options that avoid unnecessary recurring cellular fees.
Read more…..Biometric system work For the attendance of office Employees

Picking a fingerprint device that supports firmware updates or vendor cloud features can extend its useful life and reduce replacement costs.
Typical fingerprint device tiers:
- Basic entry models : cost-effective, limited capacity, local client sync.
- Mid-range models : larger capacity, better sensors, optional cloud sync.
- Advanced models : enterprise-grade sensors, faster throughput, multi-site support.
These tiers illustrate how capacity and connectivity affect price and suitability for small offices.
What Is the Price Range for Facial Recognition Attendance Systems for SMEs?
Facial recognition systems are typically pricier than basic fingerprint terminals because they need higher-resolution cameras, AI matching and more processing for contactless recognition. Entry-level face systems that handle hundreds to a few thousand users and offer contactless onboarding sit in the mid-price band good for reception areas and retail points. Mid-tier devices add AI anti-spoofing, longer-range recognition and cloud management, which raise cost but reduce friction and manual checks. Multi-site and multimodal face+fingerprint deployments sit at the top and are appropriate when security and scalability matter most.

Facial devices can cut admin time spent on manual checks, but remember to factor in network bandwidth and potential cloud storage costs when comparing total cost of ownership.
Facial device considerations:
- Entry face terminals : contactless recognition good for hygiene-sensitive sites.
- AI-enabled face devices : anti-spoofing and better performance in varied lighting.
- Multimodal face systems : combine modalities for redundancy and higher security.
Use these considerations to match facial solutions to SME budgets and operational priorities.
How Do Software Pricing Models Affect Biometric Attendance System Costs for Startups?
Software licensing and deployment choices often make up the largest recurring portion of cost: subscription (SaaS) plans bill monthly or yearly per-user or per-device, perpetual licenses require a larger one-time fee plus optional annual support, and hybrid approaches mix upfront fees with lower monthly cloud costs. Subscriptions reduce initial capital outlay and usually include hosting, updates and support; perpetual licenses lower recurring charges but typically need local infrastructure, backups and upgrade budgets. Cloud systems may add costs for storage, API usage and mobile access; on-premise setups shift those costs to servers, backups and IT staff time.

Choose between subscription and perpetual licensing based on cashflow, IT capacity and expected growth startups often prefer predictable monthly billing and quick onboarding from cloud services.
| Software Model | Billing | Example Monthly/Yearly Range | Notes (Cloud vs On-Prem) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SaaS subscription (per-user) | Per-user/month or per-device/month | $2–$10 per user/month (typical) | Cloud hosting, automatic updates, mobile apps |
| Perpetual license | One-time license + annual support | One-time fee (varies widely) + 10–20% yearly support | On-premise option, higher upfront cost |
| Per-device/subscription | Per-device/month | $5–$25 per device/month | Useful for kiosks and multi-site setups |
This table highlights that SaaS spreads costs over time while perpetual licensing concentrates them up front; startups should weigh cashflow and scaling needs when choosing a model.
Beyond price, compare operational impact: SaaS reduces IT burden and speeds deployment, while on‑premise gives tighter data control but requires more maintenance.
- Billing unit : per-user vs per-device changes totals as headcount grows.
- Feature tiers : payroll exports, biometric analytics, API access.
- Support and SLAs : faster SLAs typically cost more.
These items determine whether subscription pricing yields a better total cost of ownership for your startup.
What Are the Differences Between Subscription and Perpetual Licensing for Attendance Software?
Subscription licensing spreads costs and often includes hosting, updates and support making it easier to scale with minimal upfront capital. Perpetual licenses require a larger one-time payment and commonly charge separately for updates and support; they can be cost-effective if you have a stable headcount and in-house IT to manage servers. For small businesses with limited IT staff, subscriptions reduce hidden maintenance costs and provide vendor-managed backups and security patches. Cash-strapped startups may prefer subscriptions to avoid capital expenditure, while established firms with predictable growth might find perpetual licensing cheaper over several years.
The right choice depends on whether you prefer predictable recurring spending versus a larger initial investment, and whether you want vendor-managed operations or local control.
How Do Cloud-Based and On-Premise Software Costs Compare for Small Businesses?
Cloud-based systems often deliver lower total cost of ownership for small businesses because they remove the need for local servers, backups and continuous IT support, charging predictable monthly fees for hosting, storage and user management. On-premise deployments trade that convenience for greater local control and potentially lower long-term licensing costs if you can absorb maintenance overhead. Hidden on-prem costs include hardware refreshes, disaster recovery, security patches and dedicated personnel time; cloud solutions can add incremental charges for large storage volumes, API usage or premium integrations. For most SMEs, cloud lowers the barrier to entry and speeds ROI thanks to quicker deployment and included updates.
Use a TCO comparison that accounts for infrastructure, staff time, upgrade cycles and projected growth to decide which approach gives the best payback.
- Upfront cost : Cloud lower, on-prem higher.
- Maintenance : Cloud vendor-managed, on-prem internal.
- Scalability : Cloud scales faster with predictable pricing.
These points help small businesses balance control with predictable budgeting.
What Are the Installation, Integration, and Hidden Costs When Implementing Biometric Attendance Solutions?
Beyond hardware and software, several implementation costs can meaningfully affect your budget: professional installation and cabling, API integration with payroll/HRMS systems, staff training, network upgrades and data-compliance work. Integration may be straightforward with off-the-shelf connectors or require custom development for legacy payroll systems custom work usually increases cost and timeline. Training and change management are often underestimated but essential to avoid attendance exceptions during rollout. Planning for warranty coverage, SLA upgrades and periodic maintenance prevents surprise expenses after launch.
Identifying these less-obvious line items early helps you avoid budget overruns and deployment delays and makes vendor proposals easier to compare on an apples-to-apples basis.
| Implementation Area | Cost Drivers | Typical Impact on Budget |
|---|---|---|
| Installation & cabling | Complexity, multi-site work, professional labor | 2–10% of project cost |
| Integration (HR/payroll) | Off-the-shelf connector vs custom API development | Connector: low; Custom: weeks of dev effort |
| Training & change mgmt | Number of managers/users, documentation | One-time training fees or vendor hourly rates |
This table shows that integration scope and installation complexity cause the largest variation in hidden costs, so clarify these items with vendors before you buy.
Common hidden costs include:
- Network upgrades : switches, Wi‑Fi extenders or bandwidth increases.
- Power and backup : UPS or dedicated circuits for terminals.
- Data retention & compliance : storage and legal review expenses.
Accounting for these extras upfront ensures a realistic budget and a smoother rollout.
What Installation and Setup Fees Should Small Businesses Expect?
Installation fees depend on device count, mounting complexity and whether new cabling or network drops are required. A single-device install on existing infrastructure can be minimal; multi-site rollouts involve travel and coordination. Professional installers typically handle physical mounting, power management, device registration and initial connectivity checks tasks that reduce deployment risk and shorten downtime compared with DIY setups. Ask vendors whether installation includes basic configuration and user onboarding and whether they offer bulk deployment discounts or on-site assistance as part of a support package. Budgeting for professional installation often pays off by preventing configuration mistakes that create payroll exceptions.
Choose DIY or professional installation based on in-house technical capability, rollout scale and how quickly you need the system live.
How Much Do Integration Fees with HR and Payroll Systems Typically Cost?
Integration fees vary widely: an out-of-the-box connector to a popular payroll package may be included or charge a modest one-time fee, while custom API work to link with a legacy HRMS requires developer time and testing that can stretch the timeline and budget. Simple field-mapping can take a few days; complex authentication and reconciliation logic may take several weeks. Also plan for ongoing maintenance costs API changes on either side can require updates. When comparing vendors, request clear estimates for standard connectors versus custom integrations and include a contingency for post-launch adjustments.
Favor vendors who document connector capabilities and offer maintenance SLAs to reduce the risk of unexpected integration costs later.
- Connector availability: Pre-built connectors reduce cost.
- Data mapping complexity: payroll fields and overtime rules increase effort.
- Ongoing maintenance: API changes may require paid updates.
These factors shape both initial integration expense and future operational costs.
How Can Small Businesses Calculate the ROI of Biometric Attendance Systems?
Calculate ROI by comparing annualized costs (hardware amortization, software subscriptions or support, installation and maintenance) against quantifiable savings from reduced time theft, fewer payroll corrections and administrative time reclaimed. A simple ROI formula: (Annual Savings − Annual Costs) / Annual Costs, with payback expressed in months. Savings usually come from reduced unauthorized overtime, elimination of buddy punching, fewer payroll disputes and less HR time spent reconciling timesheets. Run conservative and optimistic scenarios to see a range of outcomes and test how sensitive payback is to adoption and error-rate reductions.
How to choose ……………..HR Automation Software

Build a short spreadsheet listing each cost and saving this makes the decision transparent and helps you prioritize the device and software features that most affect payback.
| Cost/Saving Item | Unit / Metric | Example Impact (monthly) |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced time theft | % of payroll hours saved | 0.5–2% payroll reduction |
| Admin hours saved | Hours/month | 10–40 hours saved (HR time) |
| Payroll error reduction | $ per month | Reduced corrections, e.g., $200–$1,000 |
The table shows how modest cuts in payroll leakage and reasonable HR time savings can add up to meaningful annual returns for small businesses.
Steps to calculate ROI:
- List all costs : amortized hardware, software, install, maintenance.
- Estimate savings : time-theft reduction, admin hours, fewer corrections.
- Compute payback : months to recover the initial investment.
These steps give a practical way to decide whether a biometric investment meets your financial goals.
What Savings Result from Reducing Time Theft and Buddy Punching?
Cutting time theft and buddy punching directly reduces payroll overpayments and manual corrections; industry studies show measurable payroll leakage that biometric controls can largely prevent. For example, if a business estimates 1% payroll leakage from buddy punching, stopping half of that leakage yields direct monthly cash savings that add up over a year. Biometric systems discourage proxy clock-ins because a fingerprint or face check ties each log to a unique identity, greatly reducing fraudulent entries. Quantify expected leakage reduction before purchase to set realistic ROI expectations and choose the modality that best prevents the behavior you see.
Research further underscores the clear advantages biometric systems offer in reducing payroll inefficiencies and improving operational accuracy.
Biometric Attendance Benefits: Time Theft, Payroll, ProductivityBiometric attendance systems help businesses reduce employee time theft by using unique personal characteristics that cannot be duplicated. Unlike manual attendance methods, which need constant oversight, biometric systems save staff time, lower staffing overhead and provide accurate labor data for payroll—helping operations run more efficiently and boosting productivity. The benefits of implementation of biometric attendance system, GM Mir, 2018
Tangible payroll savings combined with fewer administrative reconciliations often lead to payback measured in months rather than years for small businesses with recurring hourly payroll.
How Does Improved Payroll Accuracy and Administrative Efficiency Impact ROI?
Better payroll accuracy reduces late corrections, audit work and employee disputes, while automating time capture and payroll exports frees HR staff from manual data entry. Conservatively estimating reclaimed HR time say 10–20 hours per month translates into clear salary-cost savings or redeployment of staff to higher-value tasks. Fewer payroll errors also cut indirect costs like incorrect overtime payments and regulatory exposure from misreported hours. These improvements provide a steady, recurring boost to ROI that compounds with each year of reliable operation.
When you calculate ROI, include both hard dollar payroll savings and softer benefits from better staff allocation and less time spent resolving disputes.
Which Factors Influence the Total Cost of Biometric Attendance Systems for Small Businesses?
Several factors shape final cost: biometric modality (fingerprint, face, multimodal), device features (AI camera, capacity, throughput), number of devices and their placement, software licensing model, integration complexity and vendor support levels including warranty and SLAs. Employee count and growth expectations determine device-to-user ratios and licensing needs; multi-site deployments increase installation and connectivity costs. Vendor offerings can change the equation some bundle cloud software and mobile apps with devices, lowering total cost and speeding deployment. Evaluate these factors together to build a realistic budget that covers both initial and recurring expenses.
Use a prioritized checklist of these cost drivers so you can weigh trade-offs and choose the hardware, software and services that match both your budget and goals.
- Modality and features : higher accuracy and AI increase device cost.
- Scale : more employees and sites raise hardware and licensing needs.
- Integration scope : custom integrations add time and fees.
These drivers guide procurement choices and help forecast future budget needs.
How Do Biometric Modalities and Device Features Affect Pricing?
Modality is the single largest hardware driver: fingerprint-only devices cost less because sensors are simpler, while facial systems require better optics and processing, which raises price. Premium features AI anti-spoofing, dual cameras, multimodal support and industrial housings—push unit cost higher but reduce false rejects and improve user experience. For small businesses, focus on essential features that solve real problems (for example, hygiene or noisy environments) to avoid overpaying for bells and whistles. Mapping features to price helps prioritize investments that improve throughput and reduce administrative work.
Match modality to your use case so you pay for value rather than unnecessary extras.
What Role Do Employee Count and Scalability Play in Cost Determination?
Employee count sets the minimum device capacity and the number of devices needed for comfortable entry/exit throughput, while scalability affects licensing and upgrade choices. Consider peak concurrency how many people will clock in at once when choosing device throughput and placement. Per-user licensing can rapidly increase costs for growing teams; per-device plans or site licenses may be more economical at scale. Budget for growth with scalable cloud subscriptions or modular device additions to avoid costly rip-and-replace upgrades later.
Plan device-to-employee ratios and licensing tiers based on projected growth to keep incremental costs predictable.
Why Choose Tipsoi’s Biometric Attendance Solutions for Your Small Business Budget?
Tipsoi focuses on IoT- and cloud-connected smart attendance systems that combine integrated hardware and cloud software for attendance and payroll workflows practical options for SMEs looking for affordable workforce management. Tipsoi’s device portfolio includes the Fastface series, TF-80 and Prompt series, covering entry-level fingerprint terminals through AI-enabled facial and multimodal devices so you can choose the right balance of price and capability. Our solutions prioritize quick recognition (face/fingerprint/RFID), mobile app support for Android and iOS, and cloud integration features that reduce deployment complexity for small businesses. Tipsoi also positions competitive device pricing (representative range: ৳12,000 to ৳100,000) and bundled services to help keep implementation costs predictable.
For small businesses evaluating vendors, Tipsoi’s integrated hardware + cloud software approach, plus optional on-site installation assistance, can shorten deployment time and cut hidden setup expenses.
What Are the Affordable Tipsoi Devices Suitable for SMEs?
Tipsoi’s product mix includes compact fingerprint terminals for single-site small offices, mid-tier facial readers for contactless entry points, and multi-modal Prompt-series devices when redundancy and security matter. These options fit SME scenarios where budget, hygiene and quick onboarding are priorities, letting you pick a model that balances capacity and cost. Warranty and basic after-sales support are included to reduce short-term maintenance uncertainty. Choose a Tipsoi device based on expected throughput, need for cloud management and whether contactless recognition is important for your workplace.
Compare device capability to your daily peak usage to match a Tipsoi model to your operational needs.
How Does Tipsoi Support Small Businesses with Installation and After-Sales Services?
Tipsoi offers installation assistance and after-sales support, including on-site installation help and a one-year machine warranty to address early operational issues. These services reduce configuration risk and speed time-to-value by ensuring devices are mounted, networked and registered with cloud services correctly. Tipsoi also provides customizable software options and mobile apps for administration and remote management, which can lower recurring IT overhead. When budgeting, include vendor support packages these can substantially reduce hidden integration and training costs.
Talk to vendors early to understand which installation and SLA tiers are included or available as add-ons so you can compare total delivered value across proposals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key benefits of using biometric attendance systems for small businesses?
Biometric attendance systems improve accuracy in tracking employee time, reduce time theft and simplify payroll processes. By using unique traits like fingerprints or facial recognition, these systems minimize buddy punching and produce reliable attendance records. They also cut administrative work by automating data collection and payroll integration, which improves operational efficiency and lowers costs over time.
How can small businesses ensure data security when using biometric systems?
Data security is essential. Choose vendors who follow data protection regulations and offer strong encryption for stored biometric data. Keep software up to date with regular patches, enforce access controls so only authorized staff can manage biometric records, and run periodic audits to spot vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with best practices.
What factors should small businesses consider when selecting a biometric attendance system?
Consider the biometric modality (fingerprint, face, etc.), scalability, and how well the system integrates with your HR or payroll software. Evaluate total cost of ownership hardware, software, installation and maintenance and pay attention to user experience such as ease of use and recognition speed, which strongly affect employee adoption.
Are there any ongoing costs associated with biometric attendance systems?
Yes. Ongoing costs can include software subscriptions, maintenance and support, cloud storage or data management fees, periodic updates, training for new hires and eventual hardware replacements. Factor these recurring expenses into your budget to understand the full financial commitment.
How can small businesses calculate the return on investment (ROI) for biometric attendance systems?
To calculate ROI, compare total annual system costs (hardware, software, installation and maintenance) against measurable savings from reduced time theft, fewer payroll errors and reclaimed admin hours. Use the formula: (Annual Savings – Annual Costs) / Annual Costs. This shows whether the system pays back and how quickly.
What are the common challenges small businesses face when implementing biometric attendance systems?
Common challenges include integrating with existing HR/payroll systems, securing employee buy-in and training, and addressing data privacy concerns. Budget constraints can limit access to higher-end systems, and technical issues during installation can disrupt operations. Mitigate these risks by researching vendors, planning training and support, and budgeting for integration work.
Conclusion
Investing in biometric attendance systems can improve payroll accuracy, reduce time theft and streamline HR processes for small businesses. By understanding the main expenses involved, you can make informed choices that match your operational needs and budget. Embrace the efficiency and reliability biometric solutions bring and explore our range of devices to find the best fit for your business.